Fig. 3.
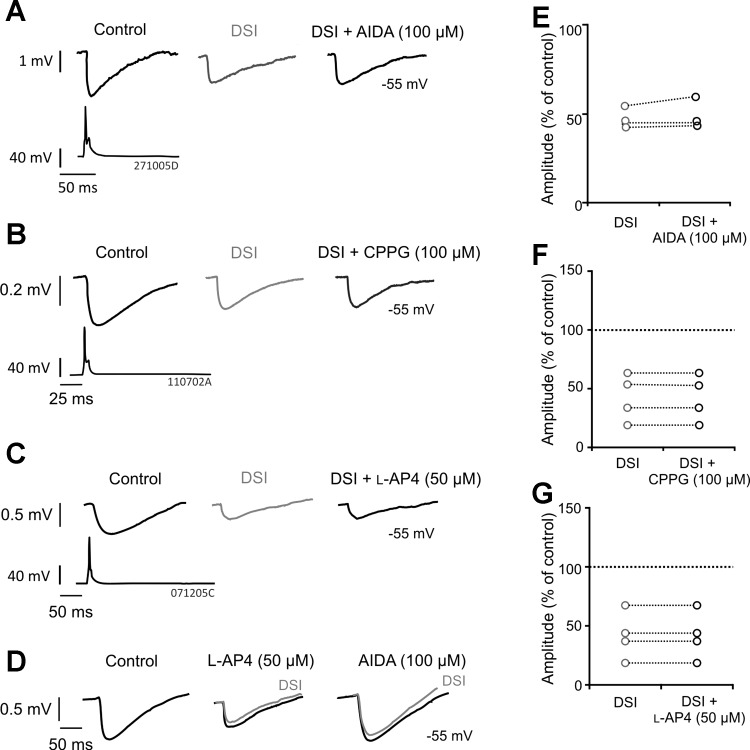
(RS)-1-aminoindan-1,5-dicarboxylic acid (AIDA), (RS)-α-cyclopropyl-4-phosphonophenylglycine (CPPG), and l-2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoate (l-AP4) do not prevent DSI at multipolar nonadapting interneuron-to-pyramidal cell connections. A–C: average IPSPs obtained from paired whole cell recordings between multipolar nonadapting interneurons and pyramidal cells during DSI and in the presence of AIDA [100 μM; postsynaptic group I metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1a) antagonist], CPPG (100 μM; group III mGluR antagonist), or l-AP4 (50 μM; group III mGluR agonist), respectively. D: positive control of l-AP4 and AIDA. The example shown was recorded in the hippocampus between a CA1 basket and pyramidal cell under similar conditions to the present study. The IPSPs illustrate cooperation of group I and III mGluRs, since l-AP4 reduced the IPSPs, occluding subsequent DSI, which was then prevented by subsequent addition of AIDA. E–G: individual pair average IPSP amplitude responses to DSI alone and DSI with AIDA, CPPG, or l-AP4, demonstrating that the drugs do not prevent DSI. Each circle represents 1 pair.
