Fig. 3.
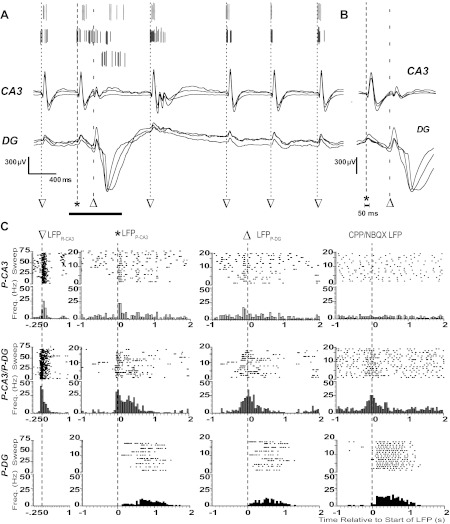
Neuronal spiking dynamics during epileptiform LFPs. A: spike-sorted APs from three example units (top) and superimposed local field potentials from three channels in CA3 (middle) and DG (bottom). Start times of LFPR-CA3 (▽), LFPP-CA3 (*), and LFPP-DG (△) are indicated with dashed lines. B: superimposed LFPs from the expanded time over the horizontal bar in A. Note that LFPP-CA3/DG and LFPR-CA3 were characterized by their presence and absence in DG, respectively. The start time of synchronous field potentials did not differ between adjacent electrodes by >50 ms, as indicated. C: raster plots for consecutive sweeps and peristimulus time histograms (PSTHs) of spike frequencies within bins centered around the start time of the indicated LFP for the three single units in A. The bin size was 50 ms for all PSTHs. Start times of LFPR-CA3, LFPP-CA3, LFPP-DG, and the CPP/NBQX LFP are indicated with dashed lines and symbols. Note that histograms show representative P-CA3 (top), P-CA3/P-DG (middle), and P-DG (bottom) units in A.
