Fig. 3.
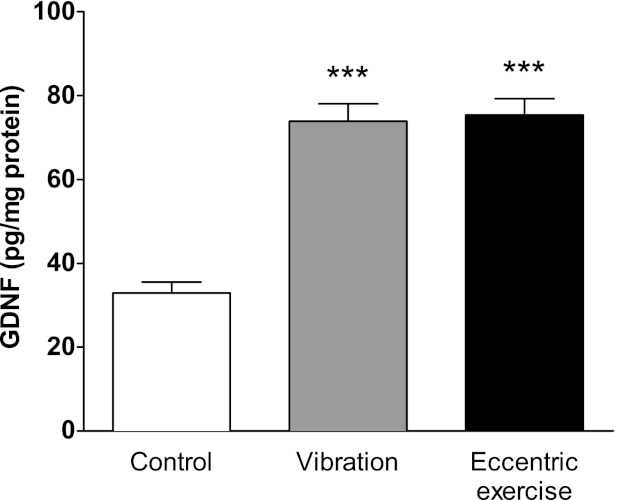
Ergonomic insults increase GDNF content in affected skeletal muscle. Rats were submitted to a hindlimb vibration or eccentric exercise. Twenty four hours later, a time point where both interventions produce muscle hyperalgesia (Alvarez et al. 2010; Alvarez et al. 2012; Dina et al. 2010), the gastrocnemius muscle was excised and GDNF content (pg/mg protein) determined by means of an ELISA procedure and compared with those exhibited by naïve rats. Both ergonomic interventions produced a significant increase in muscular content of GDNF. Comparisons between GDNF values obtained from naïve rats (white bar, n = 12) and rats submitted to vibration (grey bar, n = 7) or eccentric exercise (black bar, n = 5) were made by using a one-way ANOVA followed by a Dunnett's multiple comparisons test. ***P < 0.001.
