Fig. 5.
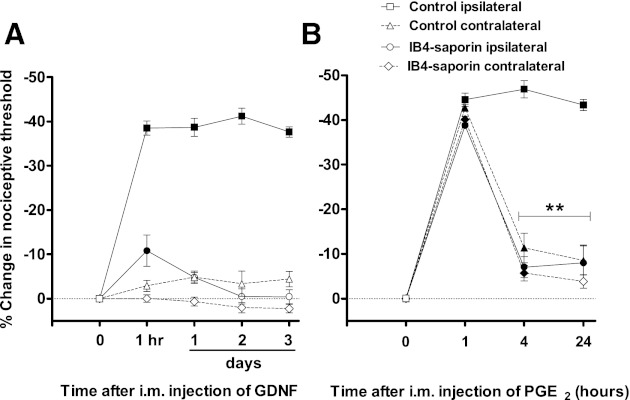
IB4-saporin abrogates acute and chronic mechanical hyperalgesia induced by GDNF intramuscularly. Rats were injected intrathecally with IB4-saporin (n = 6) or kept naïve (control group, n = 5) 10 days before unilateral GDNF injection. A: GDNF injection (10 ng/20 μl im) produced a mechanical hyperalgesia that lasted for at least 3 days in control rats (3rd day: 1,670.7 ± 30.7 mN vs. baseline: 2,674.8 ± 9.2, P < 0.001, ANOVA followed by Tukey's test). In contrast, IB4-saporin-treated rats only exhibited a modest, albeit significant, mechanical hyperalgesia that lasted ∼1 day (2,382.7 ± 11.4 mN vs. baseline: 2,669.8 ± 11.4 mN, P < 0.05, ANOVA followed by Tukey's test). B: 10 days after return to pre-GDNF baseline levels, groups were assessed for hyperalgesic priming by injecting PGE2 (1 μg/20 μl im) bilaterally. One hour after PGE2 injection, bilateral mechanical hyperalgesia was observed in naïve (1,497.4 ± 18.8 mN vs. baseline: 2,698.6 ± 7, P < 0.001, ANOVA followed by Tukey's test) and IB4(+)-saporin-treated rats (1,629.7 ± 32.9 mN vs. baseline: 2,658 ± 38.1, P < 0.001, ANOVA followed by Tukey's test). Such hyperalgesia remained unchanged after 24 h in naïve rats (1 h: 1,497.4 ± 18.8 mN vs. 24 h: 1,529.6 ± 16.6 mN, P > 0.05, ANOVA followed by Tukey's test). In contrast, PGE2-induced mechanical hyperalgesia was significantly decreased in IB4-saporin-treated rats 4 h after PGE2 injection (1 h: 1,629.7 ± 32.9 mN vs. 4 h: 2,474.2 ± 88.7 mN, P < 0.01, ANOVA followed by Tukey's test), indicating that IB4(+) nociceptors mediate hyperalgesic priming. Data are plotted as %change in mechanical nociceptive threshold compared with baseline. Solid symbols represent P < 0.05 respect to baseline. Differences in nociceptive responses comparing readings taken at 1, 4, and 24 h are represented by **P < 0.01.
