Figure 2.
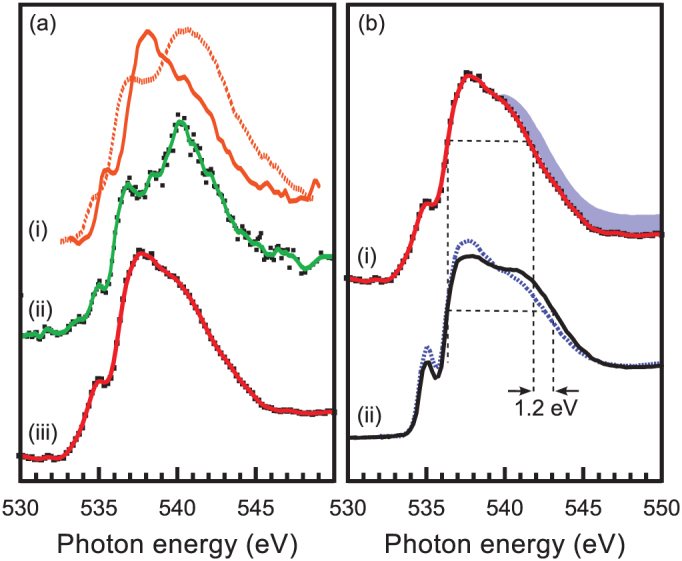
(a) Comparison of XAS spectra of (i) bulk ice Ih (dashed), ice VII (IVII) (solid)30 with the spectra of (ii) 2 ML crystalline ice and (iii) supercooled water on BaF2(111) at 1.5 Torr at 259 K (90% RH). Crystalline ice on BaF2(111) was prepared by annealing 10 ML LDA to 175 K. XAS spectra of crystalline ice on BaF2(111) were recorded via exciting with in-plane polarized light. (b) Comparison of XAS spectra of (i) supercooled water on BaF2(111) at 1.5 Torr at 259 K (90% RH) with (ii, solid) liquid water, and (ii, dashed) 6 M NaCl solution measured at room temperature31. The supercooled water spectrum is an average of two spectra obtained using in-plane and out-of-plane polarizations, shown in Fig. 1. The shaded area represents the difference between bulk ambient liquid and thin-film water. XAS spectra of liquid water and the 6 M NaCl solution were recorded in transmission mode31. The sample was embedded between two Si3N4 windows separated by a 300 nm thick spacer. All spectra are normalized by area.
