Fig. 1. Phenotype of salm and salr mutant wings and development of the Sal domain of expression in wild type and sal mutant discs and pupal wings.
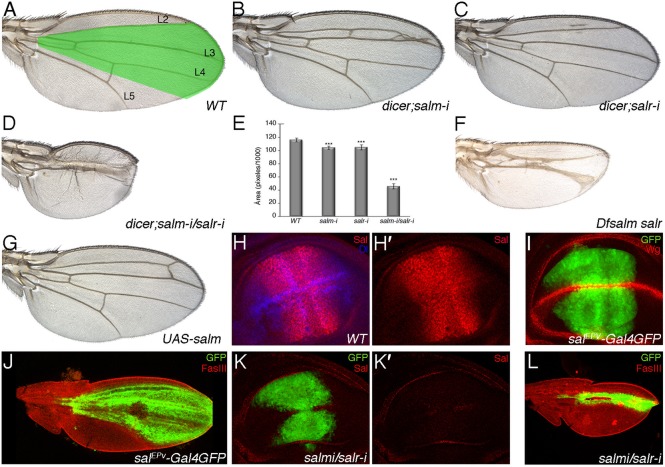
(A) Wild type wing showing the territory of salm/salr expression (green shadowing) and the longitudinal veins L2 to L5. (B,C) Phenotype of loss of salm and salr in flies of genotype UAS-dicer2/+; salEPv-Gal4 UAS-GFP/UAS-salm-i (salm-i in B) and UAS-dicer2/+; salEPv-Gal4 UAS-GFP/+; UAS-salr-i/+ (salr-i in C). (D) Loss of both genes (UAS-dicer2/+; salEPv-Gal4 UAS-GFP/UAS-salm-i; UAS-salr-i/+) results in a much stronger phenotype of wing size reduction and in the loss of the L2 and L4 veins. (E) Quantification of wing size (measured in pixels/1000) in 10 wings of WT, UAS-dicer2/+; salEPv-Gal4 UAS-GFP/UAS-salm-i, UAS-dicer2/+; salEPv-Gal4 UAS-GFP/+; UAS-salr-i/+ and UAS-dicer2/+; salEPv-Gal4 UAS-GFP/UAS-salm-i; UAS-salr-i/+. Bars represent mean ± SEM. ***p-value<0.005. (F) Mosaic wing of 638-Gal4/+; FRT40A Df(2L)32FP5/FRT40A M(2)z; UAS-FLP/+ genotype. In these wings most of the wing blade is homozygous for the salm and salr deficiency. (G) Wing of salEPv-Gal4; UAS-salm/+ genotype, showing that over-expression of salm in its normal domain of expression only causes small perturbations in the pattern of the L2 vein. (H) Expression of Salm (red) and Dl (blue) in a wild type third instar wing imaginal disc. The expression of only Salm is shown in H′. (I) Expression of GFP (green) and Wg (red) in a UAS-dicer2/+; salEPv-Gal4 UAS-GFP/+ third instar wing imaginal disc. (J) Expression of GFP (green) and FasIII (red) in a UAS-dicer2/+; salEPv-Gal4 UAS-GFP/+ pupal wing 36–40 hours APF. (K,K′) Expression of GFP (green) and Salm (red) in a UAS-dicer2/+; salEPv-Gal4 UAS-GFP/UAS-salm-i; UAS-salr-i/+ third instar wing imaginal disc. The expression of Salm is totally lost (red channel shown in K′). (L) Expression of GFP (green) and FasIII (red) in a UAS-dicer2/+; salEPv-Gal4 UAS-GFP/UAS-salm-i; UAS-salr-i/+ pupal wing 36–40 hours APF.
