Fig. 7. Correction of increased Dpp signalling by loss of salm/salr expression.
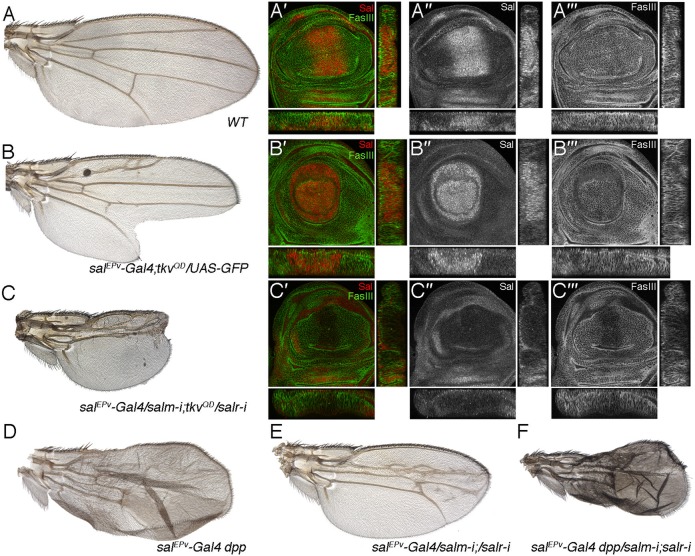
(A–A‴) Wild type wing (A) and third instar wing imaginal disc showing the expression of Salm (red in A′ and single channel in A″) and FasIII (green in A′ and single channel in A‴). Below and to the right of each image are the transversal and longitudinal sections of each disc. (B–B‴) Wing of salEPv-Gal4/+; UAS-tkvQD/UAS-GFP genotype (B) and third instar wing imaginal disc of the same genotype showing the expression of Salm (red in B′ and single channel in B″) and FasIII (green in B′ and single channel in B‴). Below and to the right of each image are the transversal and longitudinal sections of each disc. (C–C‴) Wing of salEPv-Gal4/UAS-salm-i; UAS-salr-i/UAS-tkvQD (C) and corresponding third instar wing disc showing the expression of Salm (red in C′ and single channel in C″) and FasIII (green in C′ and single channel in C‴). Below and to the right of each image are the transversal and longitudinal sections of each disc. The phenotype of these wings, and the expression of FasIII are similar to those observed in wings and discs where only the expression of sal genes is reduced. (D–F) Wings of genetic combinations between overexpression of Dpp (salEPv-Gal4 UAS-dppGFP/+; D) and reduction of salm/salr (salEPv-Gal4/UAS-salm-i; UAS-salr-i/+; E). The combination of these two conditions (salEPv-Gal4 UAS-dppGFP/UAS-salm-i; UAS-salr-i/+; F) results in wings of reduced size that differentiates the same pattern of extra-veins typical of wings over-expressing Dpp (shown in D).
