Figure 2.
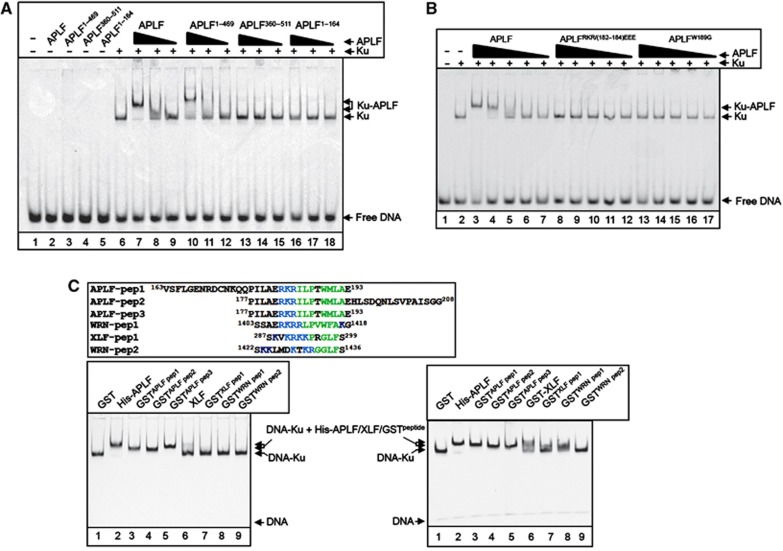
The Ku-binding motif is a novel autonomous module for recruiting proteins into Ku-DNA complexes. (A) The MID domain is required for APLF recruitment into DNA complexes containing Ku. A Cy3-labelled 30-bp duplex oligonucleotide (10 nM) harbouring blunt-ended termini was incubated with (+) or without (−) recombinant Ku70/80 (20 nM) in the absence (−) or presence of 150, 50, or 17 nM of the indicated recombinant APLF protein and employed in EMSA. Where a single concentration of APLF is indicated, the protein was employed at 150 nM. The composition of the protein DNA complexes is indicated on the right (arrows). (B) The Ku-binding motif is required for APLF recruitment into DNA complexes containing Ku. EMSAs were conducted as above. Where indicated, Ku70/80 was present at 20 nM and the indicated wild-type and mutant APLF proteins were employed at 150, 50, 17, 6 and 2 nM. (C) The Ku-binding motif is an autonomous module for protein recruitment into Ku-DNA complexes. Top left, alignment of the peptide sequences from APLF, XLF, and WRN that were fused to GST and analysed in the bottom panels, by EMSA. The conserved basic and hydrophobic patches that characterise the Ku-binding motif are indicated in blue and green, respectively. Bottom left, Cy3-labelled 30-bp duplex oligonucleotide (10 nM) was incubated with Ku70/80 (10 nM) in the presence of 0.5 μM of GST, the indicated GST peptides, full-length His-APLF (lane 2), or full-length XLF (lane 6), and employed in EMSAs as described above. Bottom right, Cy3-labelled 30-bp duplex oligonucleotide was incubated as above in the presence of GST (3 μM), His-APLF (0.5 μM), GST-XLF (1.6 μM), or the indicated GST-APLF (1.3 μM), GST-XLF (1.6 μM), or GST-WRN (3 μM) peptides.
