Figure 3.
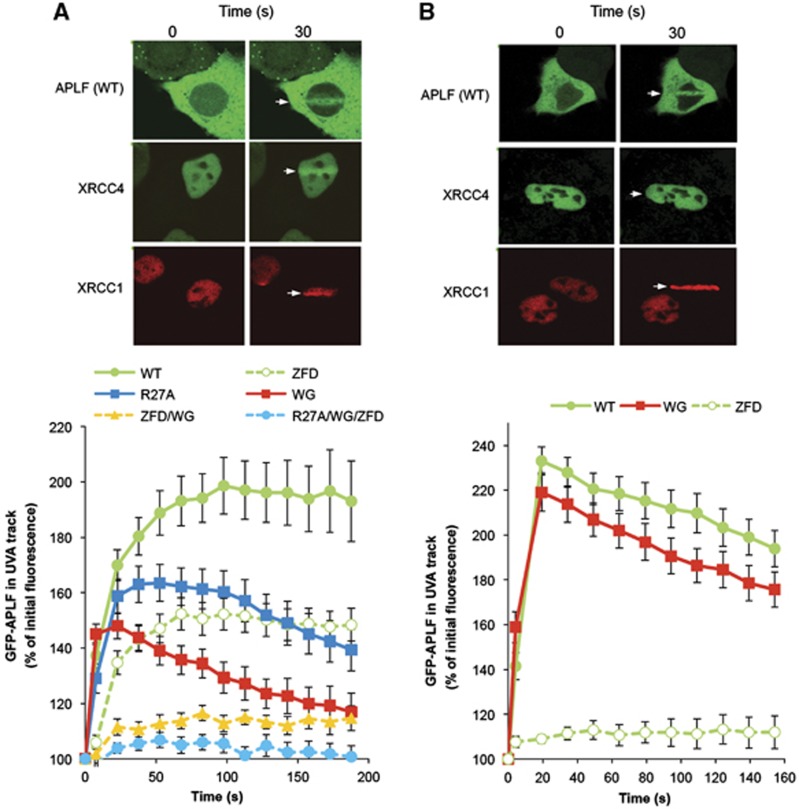
The Ku80-binding motif promotes APLF accumulation at chromosome damage. A549 cells were transiently transfected with constructs encoding wild-type YFP-APLF (WT) or YFP-APLF harbouring point mutations in the PBZ domain (YFP-APLFZFD; ‘ZFD’), FHA domain (YFP-APLFR27A; ‘R27A’), Ku-binding motif (YFP-APLFW189G; ‘WG’), or in combinations of these (‘ZFD/WG’, ‘R27A/WG/ZFD’). mRFP-XRCC1 and GFP-XRCC4 were used as markers of recruitment to single- and double-strand breaks, respectively. Cells were irradiated with 4.36 J/m2 (A) or 0.22 J/m2 (B) using a UVA laser (arrow). Images were captured at 15 s intervals after laser irradiation. For each data point, data are normalised to the YFP fluorescence intensity prior to irradiation (set to 100%). Data are the mean (±s.e.m.) of 10 or more individual cells per data point. Representative examples of YFP-APLF, GFP-XRCC4, and mRFP-XRCC1 accumulation at sites of UVA laser damage are shown (top).
