Figure 4.
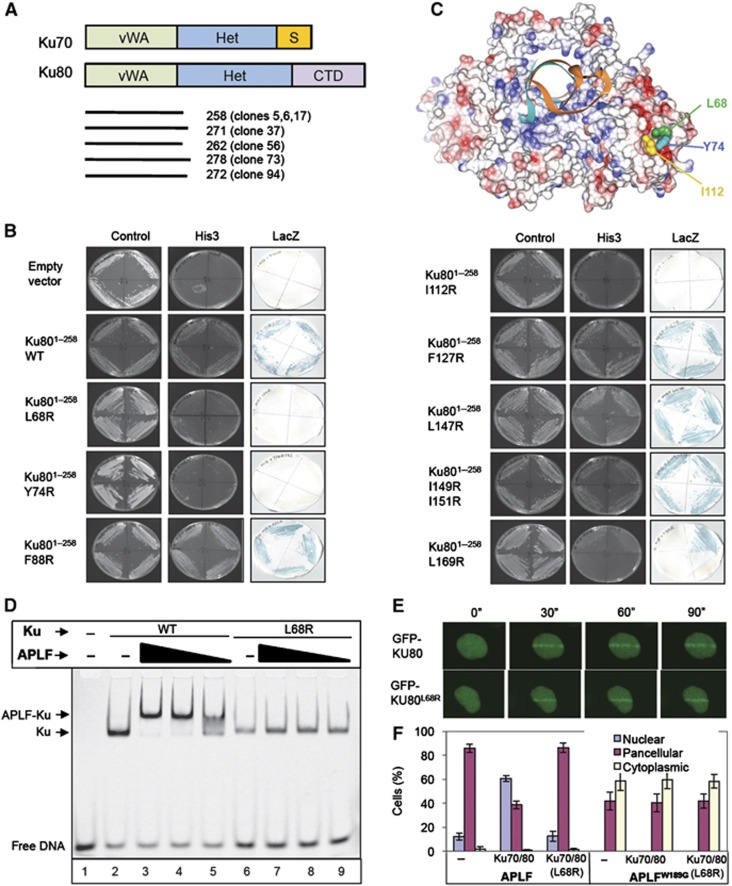
APLF interacts with the vWA domain of Ku80. (A) Cartoon of Ku70 and Ku80, depicting the von Willebrand-like (‘vWA’) domains, heterodimerisation domains (‘Het’), Ku70 SAP domain (‘S’), and Ku80 C-terminal domain (‘CTD’). The regions of Ku80 recovered by APLF in the Y2H screen depicted in Figure 1A are shown (bottom). (B) Mutation of the Ku80 vWA domain disrupts interaction with APLF. Y190 cells harbouring empty pGBKT7 or pGBKT7-APLF94–358 (encoding the MID domain) and either empty pACT2 or the indicated wild-type or mutant derivative of pACT-Ku801–258 (clone 5) were examined for His3 and LacZ reporter gene expression. (C) Residues required for APLF interaction co-localise in a hydrophobic interface on the surface of the Ku80 vWA domain. The location of L68, Y74, and I112 within the Ku heterodimer (RCSB PDB entry; 1JEY) (Walker et al, 2001) is shown. Blue and red denote basic and acidic regions, respectively. (D) Mutation of the Ku80 vWA domain prevents recruitment of APLF into DNA complexes containing Ku. A Cy3-labelled 30-bp duplex (10 nM) was incubated with (+) or without (−) 10 nM wild-type Ku (Ku70/80Δ) or mutant Ku (Ku70/80ΔL68R) in the absence (−) or presence of 700, 350, or 175 nM of the indicated recombinant APLF protein and employed in EMSA. (E) Normal accumulation of Ku70/GFP-Ku80L68R at sites of chromosome damage. A549 cells were transiently co-transfected with His-Ku70 and either GFP-Ku80 or GFP-Ku80L68R prior to UVA laser irradiation. Images were captured at 30 s intervals after laser irradiation. (F) Impact of mutations in the vWA domain on the subcellular localisation of APLF. mRFP localisation following co-transfection with mRFP-APLF or mRFP-APLFW189G and GFP vector, GFP-Ku70/GFP-Ku80, or GFP-Ku70/GFP-Ku80L68R. Data are the mean of three independent experiments (±s.e.m.).
