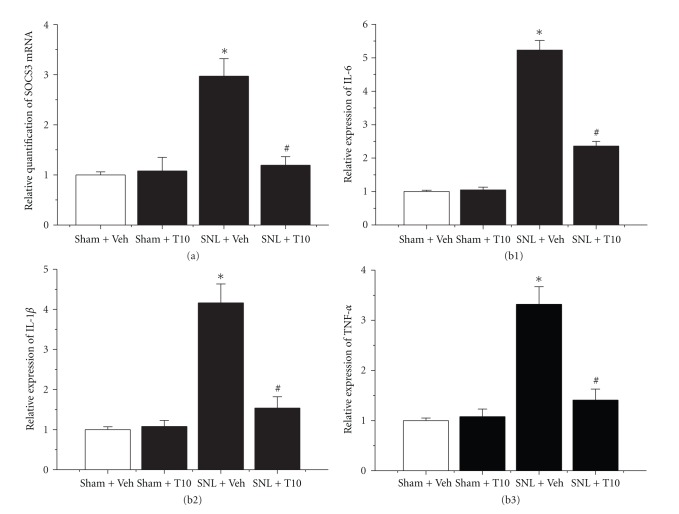
Figure 5.
The effects of intrathecal triptolide on the STAT3 target gene SOCS3 (a) and markers associated with spinal cord inflammatory state ((b1)–(b3)). (a) SOCS3 mRNA levels in rats that received different treatments were determined in the ipsilateral L4–L5 segment of the SDH using semiquantitative RT-PCR. SNL injury resulted in increased SOCS3 mRNA expression at 6 d after surgery in the ipsilateral SDH. This effect was prevented by treatment with triptolide (10 μg/kg). (b) The protein levels of the proinflammatory cytokines interleukin 6 (b1), interleukin-1 β (b2), and tumour necrosis factor-α (b3) were determined in the ipsilateral L4–L5 segment of the dorsal spinal cord in rats that received different treatments using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. These cytokines were increased at POD 6 in the ipsilateral SDH. SNL-induced increases of proinflammatory cytokine expression were prevented by the treatment with triptolide (10 μg/kg). SNL, spinal nerve ligation; SDH, spinal dorsal horn; POD, postoperative day. *P < 0.05, SNL-Veh group versus Sham-Veh group; # P < 0.05, SNL-T10 group versus SNL-Veh group. The levels of SOCS3 mRNA and proinflammatory cytokines are expressed as relative fold changes compared to the Sham-Veh group. Each group consisted of four rats.