FIG. 8.
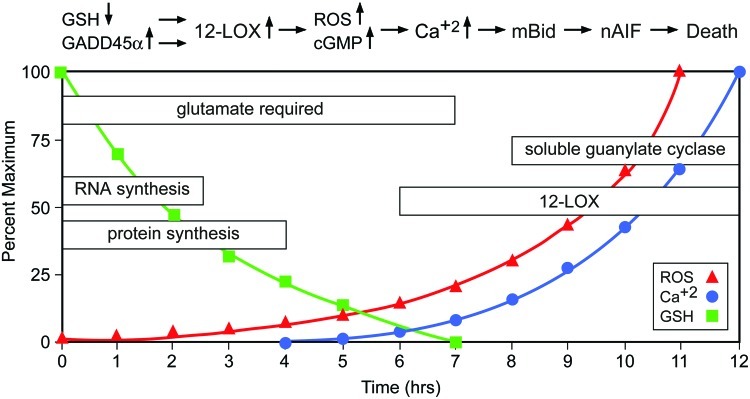
Oxidative glutamate toxicity—neuronal cell death induced by system xc− inhibition in vitro. In hippocampal HT22 cells, glutamate-mediated inhibition of cystine uptake via system xc− causes a decrease of intracellular GSH. GSH levels below 20% lead to an increase of ROS. In the early phase, de novo synthesis of RNA and proteins is necessary. One of the proteins induced is GADD45α. 12-lipoxygenase (12-LOX) and soluble guanylate cyclase are activated and mediate an accumulation of ROS and cGMP, and, subsequently, Ca++ influx. Ca++ induces cell death mediated by truncated BH3-interacting domain death agonist (Bid) and nuclear translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor (nAIF) (To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars.)
