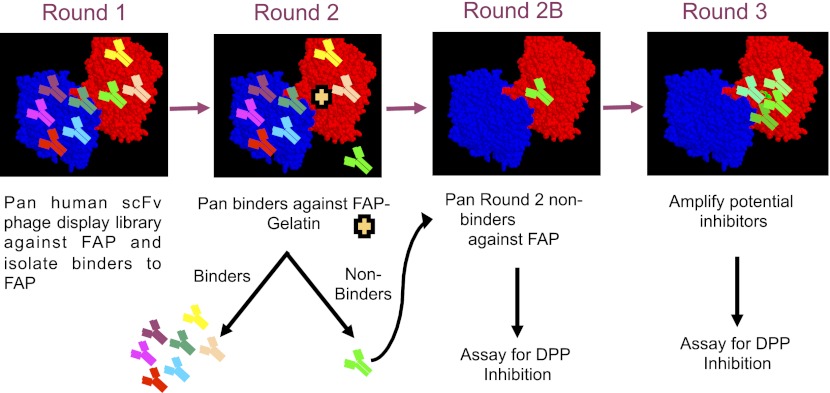
Figure 2.
Panning strategy for identification of scFv antibodies that block substrates. Human scFv phage display library was incubated with FAP-coated immunotubes. The first round of panning selected for all scFvs that bind to FAP. This includes scFvs that bind to the catalytic site of FAP (bright green) and all other noncatalytic epitopes of FAP (other colors). In the second round of panning, gelatin was incubated to competitively block access of FAP catalytic sites to the catalytic scFvs (bright green). This strategy led to the separation of these scFvs as the non-catalytic-site scFvs bound to the FAP-coated immunotubes, while the desired catalytic site FAP binders (bright green) remained in the supernatant. This supernatant containing the desired catalytic site FAP binders was then collected and repanned with FAP in round 2B in the absence of gelatin to enrich for scFvs binding to the FAP binding site. In round 3, the FAP catalytic site binders were amplified. Starting from round 2B, FAP scFv binders were expressed and evaluated for their ability to inhibit the DPP enzymatic activity.