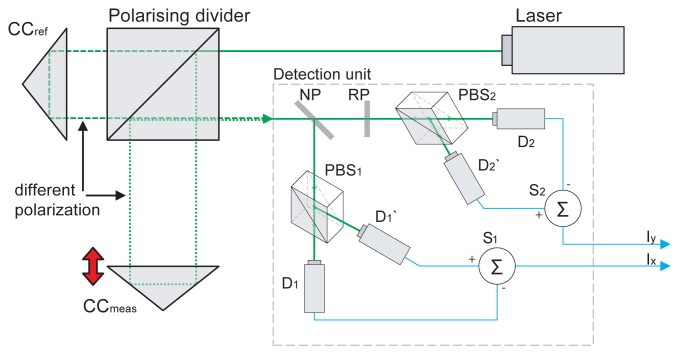
Figure 1.
Polarising laser interferometer with quadrature detection unit for homodyne detection: the interferometer employs the polarising divider, the reference corner cube reflector CCref and measurement reflector CCmeas. The output beam is compound from two beams with a different polarisation. The detection unit splits the beam into two detection branches on the non-polarising divider NP In the first branch, the polarising beam splitter PBS1 adjusts the polarisation to a single plane so that the interference occurs and is observed by photodetectors D1, D1′ (mutually in an opposite phase). In the second branch, one of the wave components is retarded by the retarder plate RP The photodetectors D2, D2′ observe the interference that occurs due to rotation of the polarisation plane on the polarising beam splitter PBS2. The subtracter SI produces the signal Ix as a difference between signals D1 and D1′, the subtracter S2 produces Iy from D2, D2′ in the same way.