Fig. 1.
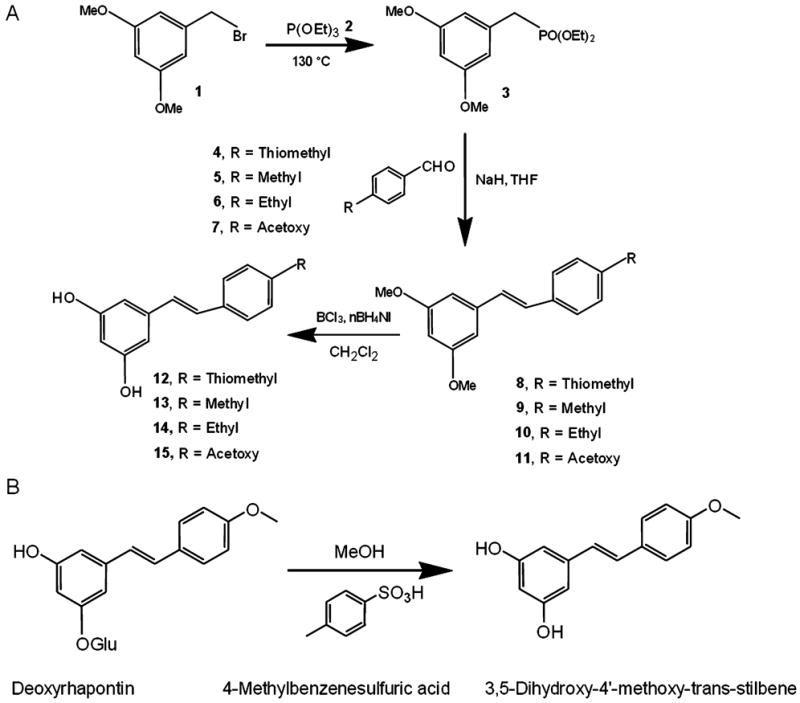
Synthesis steps for resveratrol derivatives. (A) Resveratrol Derivatives 1, 2, 3, and 5 were synthesized by a modified Horner-Emmons-based route using a diethyl phosphonate to generate stilbene (Andrus et al., 2003). 1-(Bromomethyl)-3,5-dimethoxybenzene 1 was treated with neat triethyl phosphate 2 using an Arbuzov reaction to produce diethyl (3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)methylphosphonate 3 in high yield. Coupling with 4-(methylthio)benzaldehyde 4; 4-methylbenzaldehyde 5; 4-ethylbenzaldehyde 6; 4-formylphenyl acetate 7 using sodium hydride as base in THF gave the protected stilbene 8, 9, 10, 11 in 65% yield. Boron trichloride was then used to give resveratrol derivatives 12, 13, 14, 15. (B) Derivative 4 (3,5-dihydroxy-4′-methoxy-trans-stilbene) was synthesized by hydrolysis of deoxyrhapontin (3-hydroxy-5[(E)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethenyl]phenyl hexopyranoside) treated with 4-methyl benzensulfuric acid in methanol.
