Fig. 3.
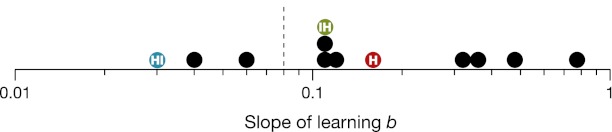
Slope of learning. Histogram of the slopes of learning in Table 1, with one symbol for each row of the table. The labeled symbols  ,
,  , and
, and  represent our identification tasks. The horizontal position of each symbol is the log-log slope b. The dashed vertical line corresponds to the dashed horizontal line in Table 1. This histogram shows the dichotomy of fast learning of unfamiliar objects and slow learning of familiar objects. We speculate that the fast learning of unfamiliar objects is learning to combine (i.e., recognize the shapes), which quickly saturates, such that, once those objects have become familiar, we are reduced to learning slowly as we gradually learn to detect the features better.
represent our identification tasks. The horizontal position of each symbol is the log-log slope b. The dashed vertical line corresponds to the dashed horizontal line in Table 1. This histogram shows the dichotomy of fast learning of unfamiliar objects and slow learning of familiar objects. We speculate that the fast learning of unfamiliar objects is learning to combine (i.e., recognize the shapes), which quickly saturates, such that, once those objects have become familiar, we are reduced to learning slowly as we gradually learn to detect the features better.
