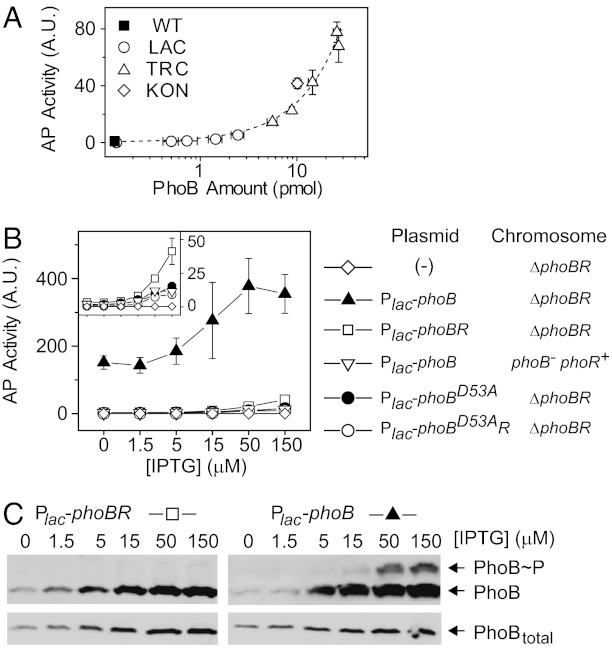
Fig. 2.
Suppression of PhoB phosphorylation by PhoR at Pi-replete conditions. (A) Dependence of basal AP activities on PhoB expression levels. PhoB and PhoR were expressed from the chromosome under different IPTG concentrations using the indicated strains. The dashed line indicates a linear trend line. (B) Effect of PhoR on basal AP activity. Indicated IPTG concentrations were used to achieve different expression levels. Strains included RU1621 (ΔphoBR) carrying pTRM11 (Plac-phoB), pRG226 (Plac-phoBR), pRG305 (Plac-phoBD53AphoR), pJZG137 (Plac-phoBD53A) or no plasmid, and RU1631 (ΔphoB) carrying pTRM11. All results are shown as the mean and SD of at least three independent experiments, and unseen error bars are smaller than symbols. (C) Effect of PhoR on phosphorylation suppression. Strains with PhoR expression (RU1621/pRG226; Left) or without PhoR (RU1621/pTRM11; Right) were grown under Pi-replete conditions. Samples were analyzed with Phos-tag gels for PhoB phosphorylation (Upper) or normal SDS gels for total PhoB levels (Lower). Phos-tag retards the migration of PhoB∼P relative to unphosphorylated PhoB.