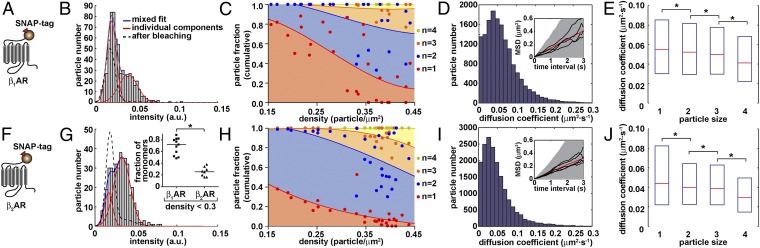
Fig. 2.
Analysis of β1- (A–E) and β2- (F–J) AR oligomerization and lateral mobility by single-molecule TIRF-M. (A and F) Schematic representation of the used SNAP-tagged constructs. (B and G) Representative intensity distributions of Alexa647-labeled particles. Particle densities were 0.24 (B) and 0.25 (G) particle/μm2. Data were fitted with a mixed Gaussian model. A mixed Gaussian fit after partial photobleaching (dashed lines) was used to precisely estimate the intensity of single fluorophores in each image sequence. (G, Inset) Comparison of the fraction of monomeric β1AR and β2AR particles at low density (0.15–0.3 particle/μm2). Each data point represents one cell. *P = 0.0003 by Mann–Whitney test. (C and H) Dependency of the distribution of particle components on particle density. Shown is the cumulative distribution of mono-, di-, tri-, and tetramers of Alexa647-labeled receptors, based on mixed Gaussian fitting analyses like those shown in B and G, as a function of particle density. Data were fitted using third-order polynomial functions to provide an indication of their trend. Each data point represents one cell. [n = 6,181 particles from 27 different cells (C) and 7,419 particles from 30 different cells (H)]. (D and I) Distribution of diffusion coefficients of receptor particles calculated from their mean square displacement (MSD). Insets, MSD plots; shown are the mean (red) as well as the 10% and 90% percentiles (shaded area) of particles that were tracked for at least 3 s; black, data of representative individual particles. (E and J) Effect of the size of GPCR complexes on their lateral diffusion. The size of individual particles was estimated on the basis of the number of bleaching steps. Shown are box plots of diffusion coefficients measured for particles of different size. The boxes encompass the 25% and 75% percentiles and median values are indicated by red lines. Differences in E and J are statistically significant by a Kruskal–Wallis test (P < 0.0001) followed by Dunn’s test (*P < 0.001).