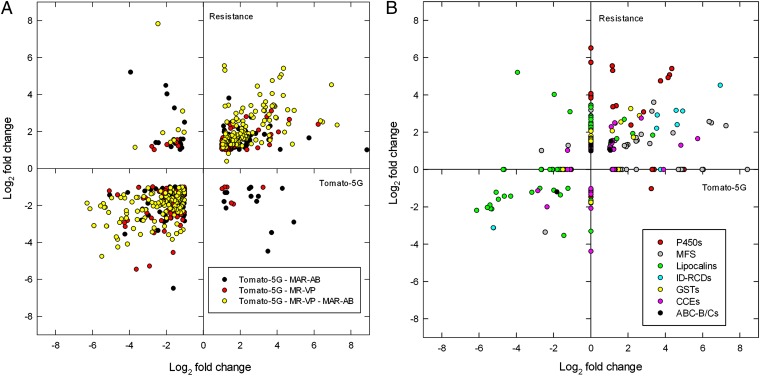
Fig. 2.
Global changes in gene expression of two multiresistant T. urticae strains (MR-VP and MAR-AB) relative to the London susceptible strain, compared with gene expression changes upon host plant change (Tomato-5G). (A) Commonly differentially expressed genes [log2(FC) ≥ 1, FDR < 0.05] in two multiresistant strains (MR-VP and/or MAR-AB: “Resistance”) and after host plant change for five generations (Tomato-5G): black, differentially expressed genes in Tomato-5G and MAR-AB; red, differentially expressed genes in Tomato-5G and MR-VP; yellow, differentially expressed genes in Tomato-5G, MR-VP, and MAR-AB (the Log2 of the average of fold changes of commonly differentially expressed genes of MR-VP and MAR-AB is plotted). (B) Fold changes of differentially expressed genes [log2(FC) ≥ 1, FDR < 0.05], known to be implicated in detoxification and transport, in two multiresistant strains (MR-VP and/or MAR-AB: Resistance) and after host plant change for five generations (Tomato-5G): red, P450 monooxygenases (P450s); black, ATP-binding cassette transporters, classes B and C (ABC-B/Cs); green, lipocalins; pink, carboxyl-cholinesterases (CCEs); yellow, glutathione S-transferases (GSTs); light blue, intradiol ring-cleavage dioxygenases (ID-RCDs); gray, MFS transporters (OrthoMCL clusters 10032, 10082, and 10236).