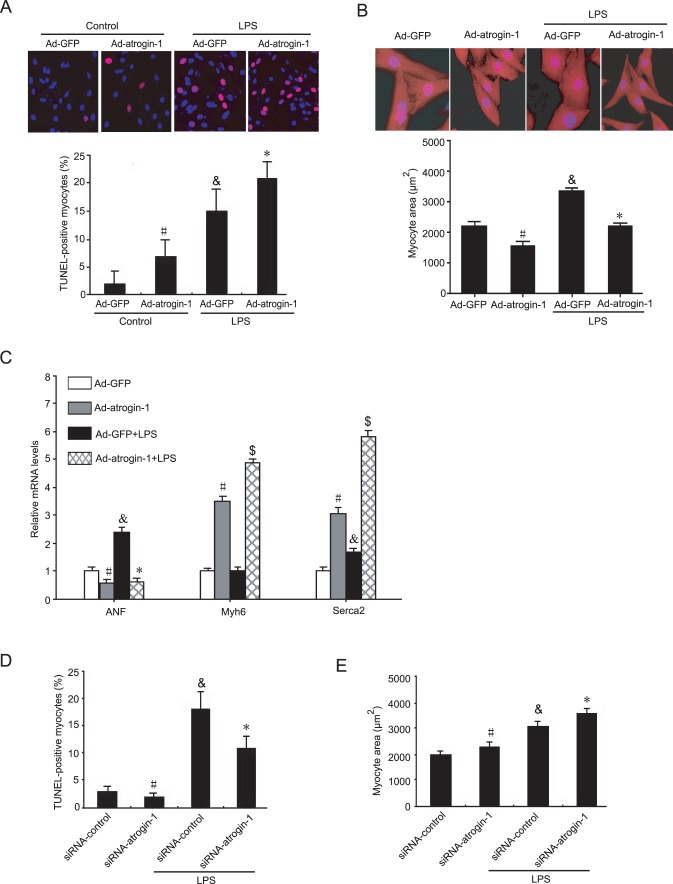
Figure 4. Effects of atrogin-1 overexpression on cardiomyocyte apoptosis and hypertrophy.
Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were infected with Ad-GFP or Ad-atrogin-1-GFP for 24 h and then treated with LPS (1 µg/ml) for additional 24 hours. A. Apoptosis was detected and quantified using TUNEL assay (red), and nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). A representative field is shown for each condition (top panels), Magnification, ×400. Quantitative analysis of TUNEL-positive cells from three independent experiments (bottom panels). B. The cells were fixed and stained with anti-α-actinin antibody followed by Alexa Fluor 568-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (red), and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). A representative field is shown for each condition (top panels), Magnification, ×200. Quantitative analysis of cell surface area (a minimum of 100 randomly chosen cells measured in each group) (bottom panels). Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 3). # P<0.05, & P<0.01 vs. Ad-GFP; *P<0.05; $ P<0.01 vs. Ad-GFP+LPS. C. The qRT-PCR analysis of ANF, Myh6 and serca2 mRNA expression was performed in triplicate using specific oligonucleotides primers. D and E. Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were infected with Ad-siRNA-atrogin-1 or Ad-siRNA-control for 24 hours. Analysis of apoptosis and cell surface area were performed as in A and B. Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 3). # P<0.05, & P<0.01 vs. siRNA-control; *P<0.05 vs. siRNA-control +LPS.