Figure 7.
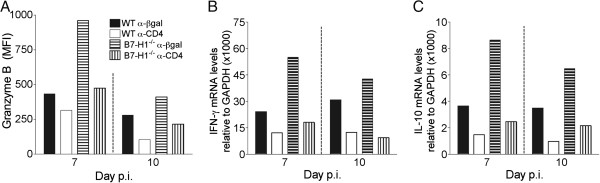
B7-H1 deficiency directly increases CD8 T-cell activity in the absence of CD4 T cells. Infected wild-type (WT) and B7-H1−/− mice were treated with α-CD4 or control α-βgalactosidase (α-βgal) monoclonal antibody at 4 and 6 days post-infection (p.i). (A) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of granzyme B expression by brain-derived virus-specific CD8 T cells (n ≥ 3/group) at days 7 and 10 p.i. Data are representative of two independent experiments with similar trends. (B,C) Relative transcript levels of (B) interferon (IFN)-γ and (C) interleukin (IL)-10 in CD8 T cells purified from brain at 7 and 10 days p.i. Transcript levels are relative to GAPDH × 1000. Data are representative of two independent experiments with similar trends.
