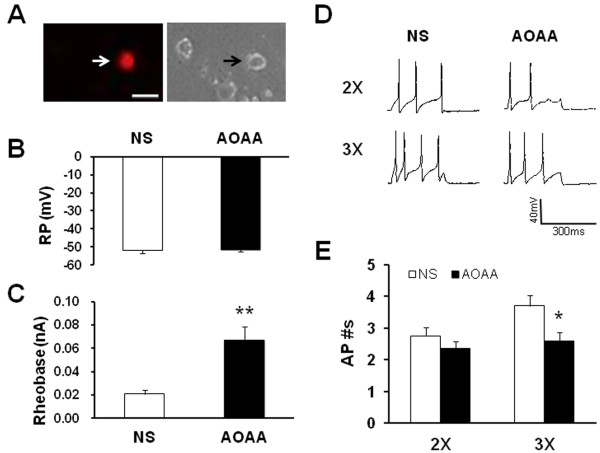
Figure 3.
CBS inhibitor AOAA reduced neuronal excitability. (A). An example of a Dil-labeled DRG neuron (Left, arrow). A phase image of the same DRG neuron is shown on the right (arrow). Bar=50 μm. Patch clamp recordings were made from Dil-labeled neurons isolated from T13-L2 DRGs. AOAA was intraperitoneally injected at the dose of AOAA 10 mg/kg body weight once a day for consecutive 7 days. (B) Administration of AOAA did not produce any effect on resting membrane potentials (RP). n=20 cells for each group. (C) Administration of AOAA, however, significantly increased rheobase when compared with NS-treated NMD rats. n=20 cells for each group; **P<0.01. (D) Representative traces of APs were induced by 300 ms depolarizing current pulses injected through the patch pipette at 2 times and 3 times rheobase in DiI labeled neurons from NS- (left) and AOAA- (right) treated NMD rats under current-clamp conditions. (E) Bar graph showed the average number of APs evoked by 3 times rheobase current stimulation was significantly reduced while the average number of APs evoked by 2 times rheobase current stimulation was not significantly reduced when compared with NS group. n=20 cells for each group; *P<0.05.