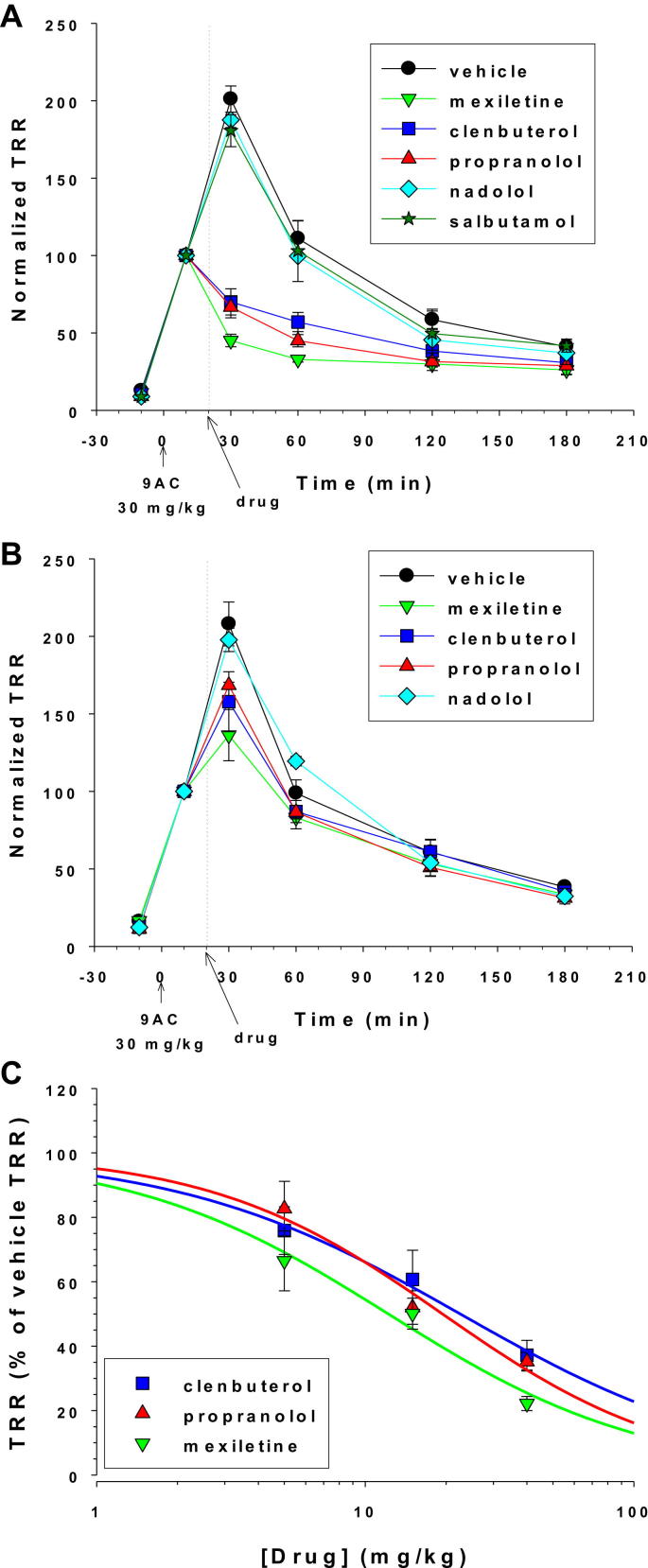
Fig. 3.
Antimyotonic effects of exploratory drugs. The time course of normalized TRR values was determined in 9-AC treated rats receiving either 40 mg/kg (A) or 5 mg/kg (B) of exploratory drugs or relative vehicle. Each curve is the mean ± S.E.M. calculated from 3-to-9 rats. Statistical comparison was performed between all the tested drugs at each time point using one-way ANOVA followed by ad-hoc Bonferroni's t-test. At 40 mg/kg, mexiletine, propranolol, and clenbuterol significantly reduced the TRR at 30-, 60-, and 120-min time points compared to vehicle (at least P < 0.05, see Section 3.2 for details). At 5 mg/kg, mexiletine, propranolol, and clenbuterol significantly reduced the TRR only at the 30-min time point. (C) The dose–response curve were constructed for mexiletine, propranolol, and clenbuterol by reporting the value of normalized TRR (expressed as percentage of normalized TRR measured in rat receiving drug vehicle alone) measured 10 min after drug administration (i.e. 30 min after 9-AC injection). The dose–response curve were fitted with equation TRR = 100/[1 + exp ([Drug]/ED50)nH], where [Drug] is the drug dose, ED50 is the half-maximum efficient dose, and nH is the slope factor. Values of fit parameters are given in Section 3.2.