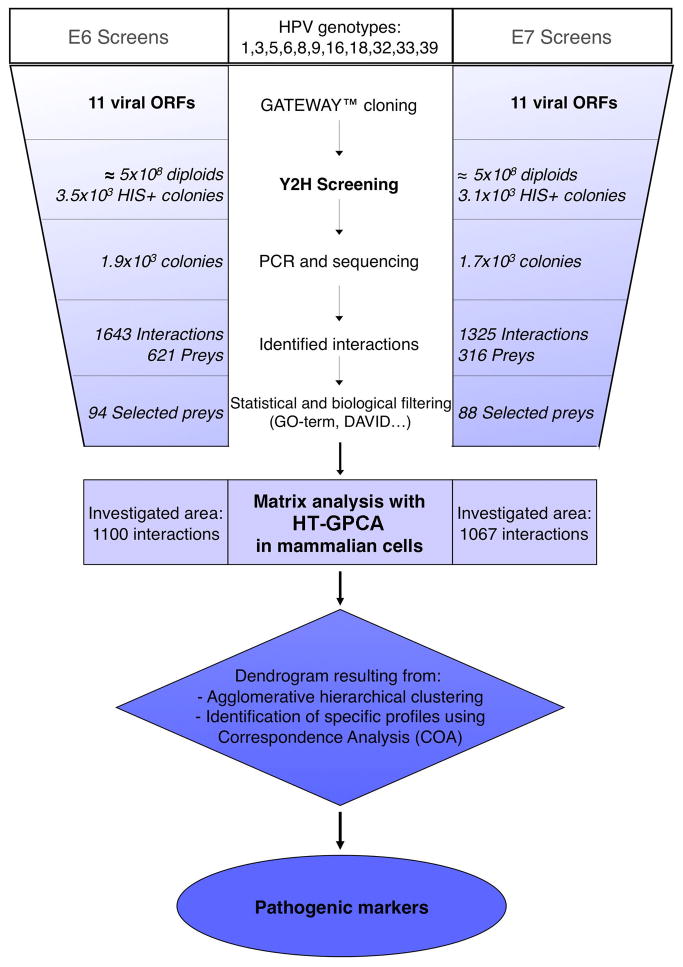
Fig. 3.
Flowchart depicting the different steps used in the comparative interactomic strategy. The 22 viral open reading frames (ORFs) corresponding to E6 and E7 proteins from 11 HPV genotypes were inserted into the pGBKT7 vector in frame with the Gal4 DNA-binding domain using a recombinatorial cloning system (Gateway®). These clones were used as bait in a high-throughput mating-based Y2H screening against a human keratinocyte cDNA library (2.5 × 106 individual clones). The cDNAs of HIS3 positive colonies were PCR amplified, sequenced and identified by BLAST. A statistical and biological filtering technique was used to select a high-confidence set of 94 preys for E6 and 88 for E7. A high-throughput mammalian interaction validation assay based on Gaussia princeps luciferase complementation (HT-GPCA) was next performed. Agglomerative Hierarchical Clustering was used to perform intergenotypic comparisons of the E6 and E7 interaction profiles and identify genotype-specific cellular targets by correspondence analysis.