Figure 5.
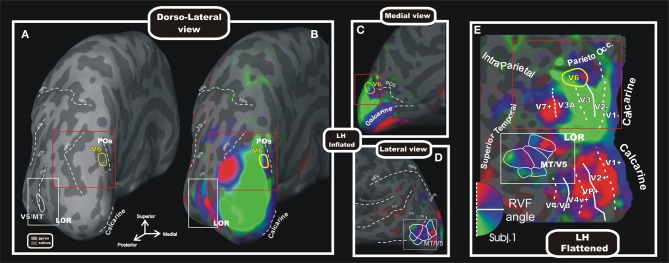
Wide field retinotopy of polar angle representation of area V6 and MT/V5 in the human brain. Inflated (A–D) and flattened (E) reconstructions of the left hemisphere (LH) of one participant are shown [modified from Pitzalis et al. (2006)]. Red and white boxes indicate trough the different views of the cortex the same parts of the brain where areas V6 and V5/MT are respectively located. Inflated cortex is shown in dorso-lateral view (A,B), and on medial (C) and lateral (D) close-ups views of the posterior brain. (A) Reference image to show the typical position of areas V6 and MT/V5 respect to the medial sulci (POs, calcarine), the pIPS and the lateral middle temporal sulci (ITs, MTs, and STs). The cortical surfaces were defined at the gray-white matter border and have been inflated to reveal regions within the sulci (concavities, dark gray) as well as on the gyri (convexities, light gray). (E) Flattened map shows retinotopic phase-encoded signal in the dorsal and ventral cortical areas (including medial V6 and lateral MT/V5). The boundaries of all visual areas were defined by mapping visual field sign (Sereno et al., 1994, 1995). Dotted and solid white lines reported on the flat maps indicate vertical and horizontal meridians, respectively. In all sections, color hue indicates the response phase, which is proportional to the polar angle of the local visual field representation: green/blue/red areas represents lower/horizontal/upper fields, respectively (see hemifield icon in E). Yellow and white outlines indicate respectively location and borders of the human area V6 (Pitzalis et al., 2006) and MT/V5 (Pitzalis et al., 2010). Red and white boxes indicate through the different views of the cortex the same parts of the brain where areas V6 and V5/MT are respectively located. Major sulci (dark gray) are labeled as follows: POs, parieto-occipital sulcus; LOR, Lateral Occipital Region; pIPs, posterior end of the intraparietal sulcus; aIPs, ascending segment of the intraparietal sulcus; hIPs, horizontal segment of the intraparietal sulcus; STs, superior temporal sulcus; MTs, middle temporal sulcus; Its, inferior temporal sulcus. On the inflated surfaces, the fundi (dashed lines) of calcarine, sylvian fissure, aIPs, hIPs, pIPs, and POs are shown.
