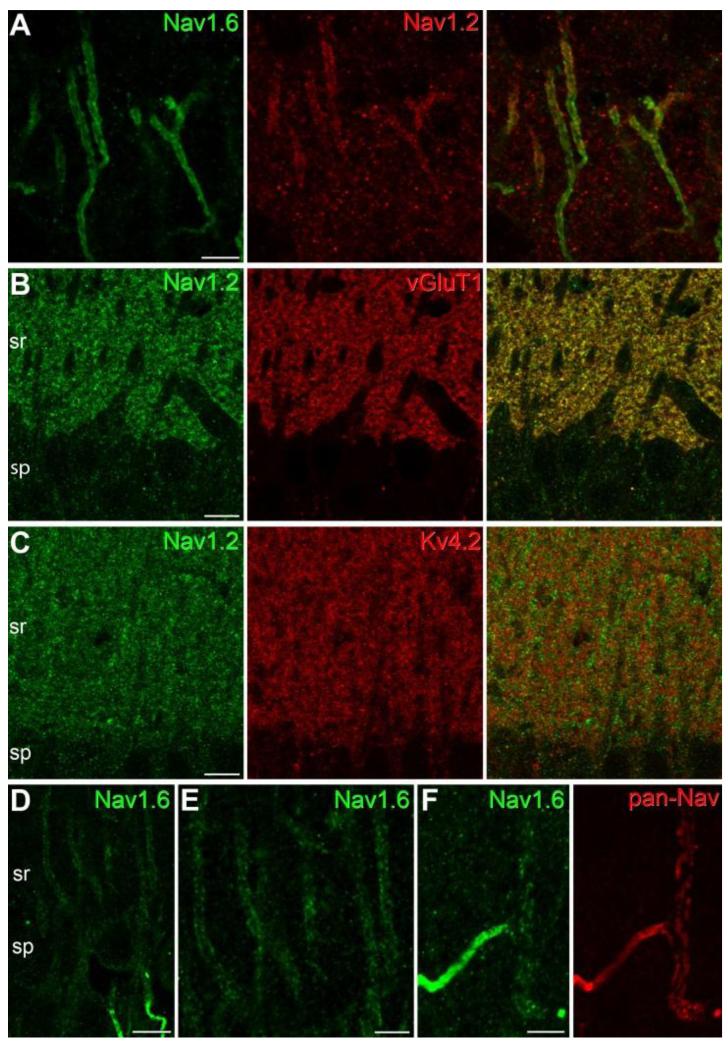
Fig. 2.
Immunofluorescence localization of the Nav1.2 and Nav1.6 subunits in CA1 PCs. (A) A double immunofluorescence reaction demonstrates the colocalization of the Nav1.6 and Nav1.2 subunits in the AISs of CA1 PCs. Immunolabeling for the Nav1.2 subunit is confined to the proximal part of the AISs. (B-C) Immunofluorescence double labeling experiments reveal that the majority of the Nav1.2 subunit immunolabeling in stratum radiatum (sr) co-localizes with the presynaptic marker vGluT1 (B), but does not co-localize with the Kv4.2 subunit (C), a K+ channel subunit that is known to be present in PC dendritic shafts and spines. (D-E) An immunofluorescence reaction for the Nav1.6 subunit in the strata pyramidale (sp) and proximal radiatum (sr) of the CA1 area demonstrates weak plasma membrane-like labeling of PC proximal apical dendrites. Note the much higher labeling intensity of the AISs. (F) A double immunofluorescence reaction in the stratum radiatum shows the colocalization of pan-Nav (red) and the Nav1.6 subunit (green) in a strongly immunopositive AIS and its parent apical dendrite. Scale bars: A, E, F, 5 μm; B-D, 10 μm.