Figure 6.
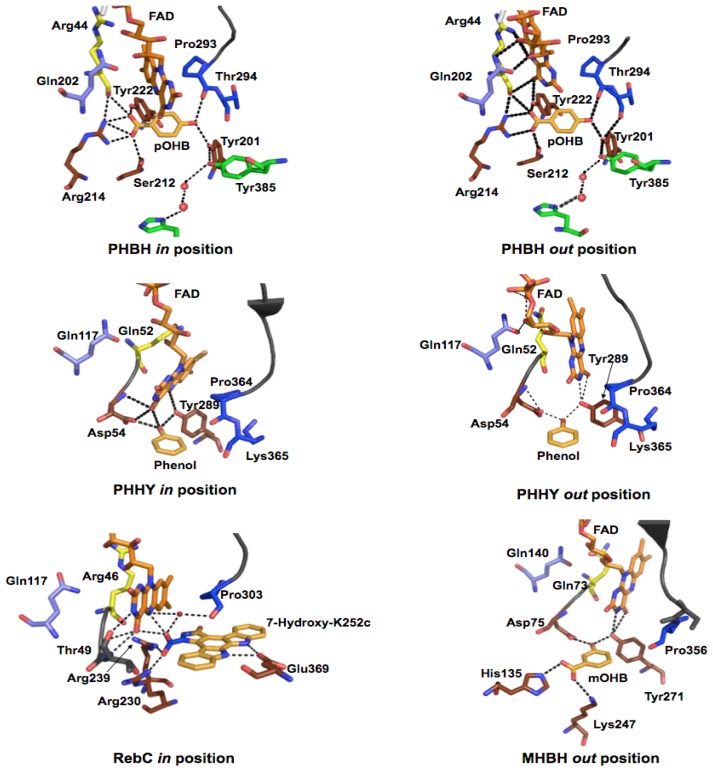
Representative target substrate binding sites and isoalloxazine ring positions for the class A external flavoprotein monooxygenases. Left—The substrate-binding pocket for PHBH, PHHY, RebC with the flavin in conformation is illustrated. In PHBH, the main chain carbonyls of Arg44 of the si-loop and Pro293 of the re-loop hydrogen-bond to each end of the aromatic substrate, pOHB. Other contacts are made with Tyr222, Arg214. Ser212, and Tyr201 to secure the target substrate. Residue Tyr201 links the substrate’s hydroxyl group in the solvent-free environment with His72 at the solvent interface by way of Tyr385 and two water molecules creating a hydrogen-bond network required for efficient catalysis. In PHHY, Asp54 of the si-loop and Tyr289 (which corresponds to Tyr222 in PHBH) make hydrogen-bond contacts with phenol as well as multiple contacts to the O(4) and N(5) of the isoalloxazine ring. No direct hydrogen-bond contacts are made between the substrate and the re-loop, only indirect contacts are made through the flavin isoalloxazine ring; Right—The substrate-binding pockets for PHBH, PHHY, and MHBH when the flavin establishes the out position. All hydrogen bonds remain the same in PHBH and PHHY except the bond from Tyr222/289 to the flavin which is reconstituted to the O(4) site in PHBH and the N(3) and O(4) site in PHHY. An additional hydrogen-bond in PHBH is made from flavin O(4) to Arg44 and from the re-strand Thr294 that lies within 3 Å of the start the hydrogen-bond network, Tyr201.