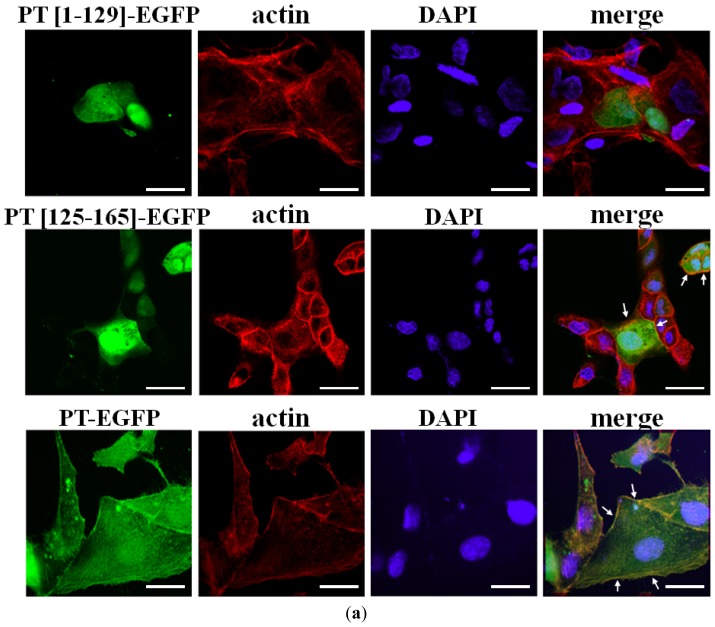
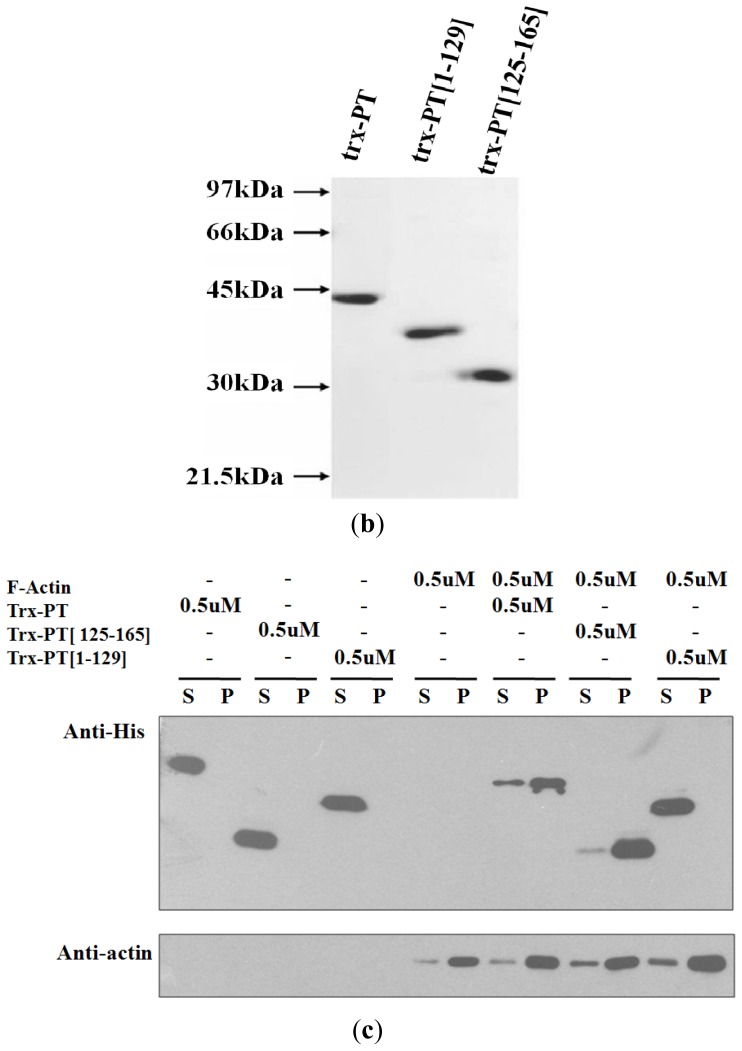
Figure 2.
Phostensin (125–165) binds to F-actin. (a) Colocalization of phostensin (125–165) and F-actin in MDCK cells. F-actin was stained with rhodamine-phalloidin. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Fluorescence for PT-EGFP (green) (or PT(1–129)-EGFP (green) or PT(125–165)-EGFP (green)), F-actin (red), and nuclei (blue) are shown on the merged images. Phostensin or PT(125–165) is conspicuously colocalized with F-actin in the cell periphery, as indicated by the arrow. The bar represents 20 μm; (b) SDS-PAGE (12.5%) analyses of trx-PT, trx-PT(1–129) and trx-PT(125–165). Molecular weight markers from top to bottom are phosphorylase b (97 kDa), bovine serum albumin (66 kDa), ovalbumin (45 kDa), carbonic anhydrase (30 kDa) and trypsin inhibitor (21.5 kDa); (c) Trx-PT(125–165) co-sediments with F-actin at high speed centrifugal forces (150,000g). Protein distributed in the pellet (p) and supernatant (s) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (12.5%). Trx-PT and trx-PT(125–165) were analyzed by western blotting with anti-(His)6 antibodies. To analyze the distribution of actin in the supernatant and pellet, the anti-(His)6 antibodies on the blotted membrane were deleted by the striping buffer (0.5 M acetic acid plus 0.5 M NaCl), and the membrane was re-blotted with anti-actin polyclonal antibodies.