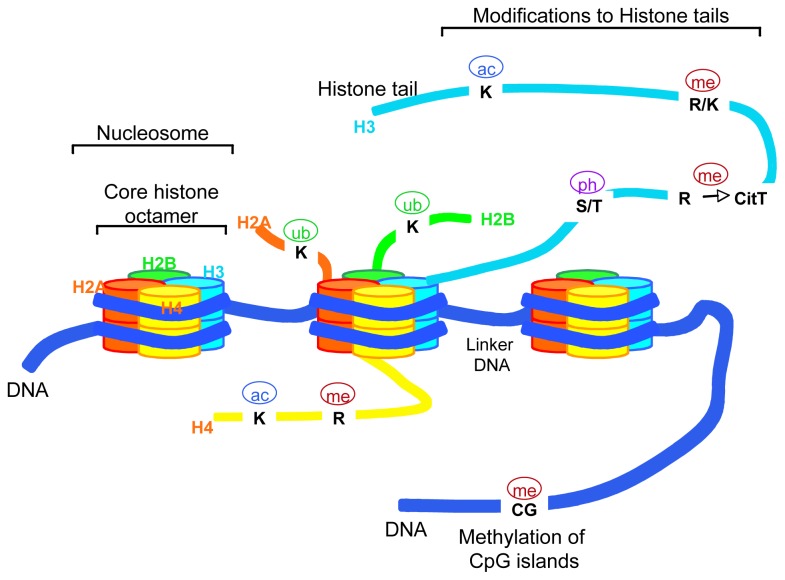
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of chromatin structure. Eukaryotic DNA is wrapped around core histone proteins (histone octamer: H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) to form compact chromatin structures termed nucleosomes. Covalent modifications to histones (on histone tails) involve amino acidic residues (Lysine (K), Arginine (R) Serine (S) and Tyrosine (T)) that can be acetylated (ac), methylated (me), phosphorylated (ph) and/or ubiquitinilated (ub). CpG islands on DNA can be methylated. These post-translational modifications result in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression.