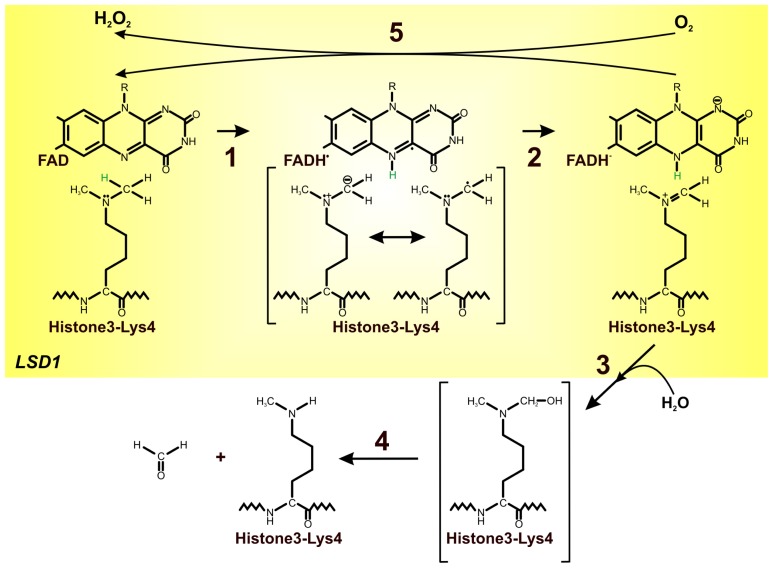
Figure 4.
Mechanism of lysine demethylation by LSD1. Simultaneous amine oxidation and flavin reduction are followed by the re-oxidation of flavin by one equivalent of molecular oxygen, producing stoichiometric hydrogen peroxide along with the formaldehyde as the demethylation by-product [48,52]. Flavin dependent amine oxidase (LSD1) catalyzes the flavin-mediated two-electron oxidation of the methylated lysine; it leads to the formation of the corresponding imine molecule with the concomitant reduction of the flavin cofactor (1, 2); following the imine formation, hydration to the N,O-hemiacetal and subsequent collapse to formaldehyde and amine takes place (3, 4); reduced FAD can be re-oxidized by molecular oxygen to hydrogen peroxide (5) [47,48,56,62,64], modified.