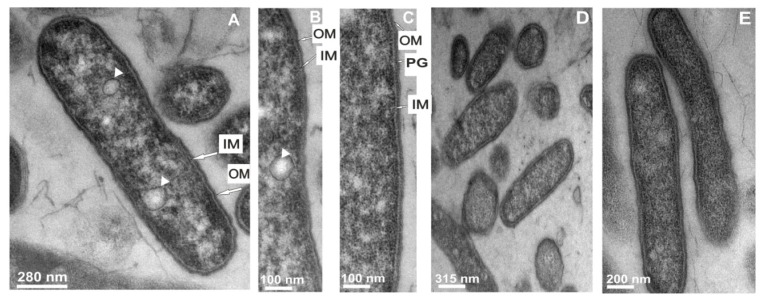
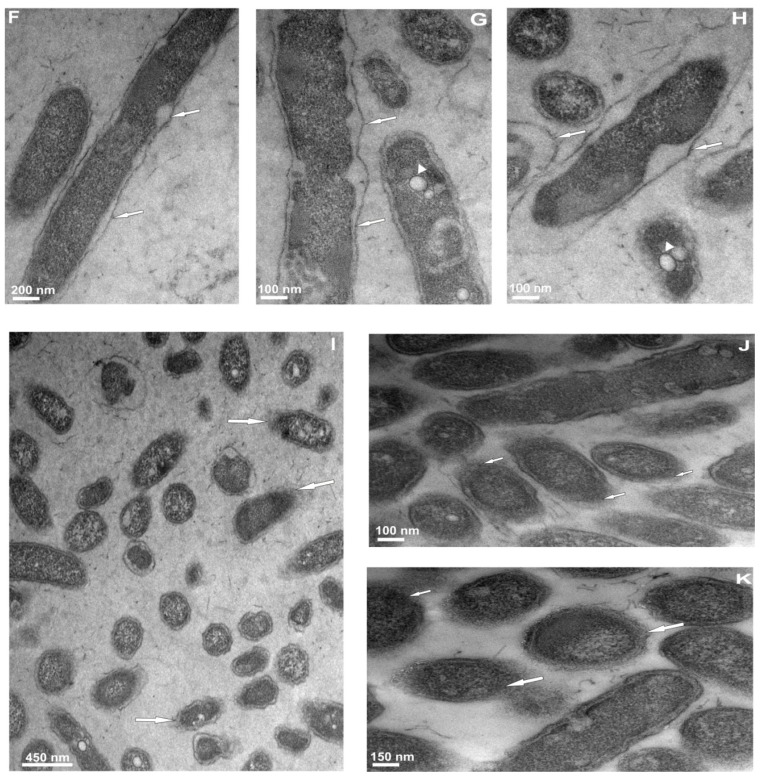
Figure 3.
The influence of the extract of G. mellonella immune hemolymph on L. dumoffii cell morphology. The cells growing on the non-supplemented (A–C,F–I) and choline-supplemented (D,E,J–K) agar medium were exposed to G. mellonella hemolymph extract (F–I,J,K) or left untreated (A–C,D,E). Then, the cells were prepared for TEM analysis as described in the Experimental Section. (A) one big bacterium in longitudinal section; vacuoles are visible inside the cell (arrowheads); the outer and inner membrane is distinguishable in the cell envelope; (B) a fragment of the bacterium with a visible internal membrane (arrows); IM, inner membrane; OM, outer membrane; (C) a portion of the bacterium with a peptidoglycan-like layer (denoted as PG); outer and inner membranes are seen; (D,E) cells cultured on the choline-supplemented medium with a typical appearance; (F) cells showing cell wall damage and a periplasmatic space (arrows); (G) bacteria with cell wall damage (arrows) and dense cytoplasm with vacuoles (arrowhead); (H) enlarged view of a bacterium with strong cell envelope damage and cytoplasm condensation; the rest of the cells exhibit cell wall damage and presence of vacuoles (arrowhead); (I) many bacterial cells demonstrating loose attachment of the cell membrane (arrows); and (J,K) cells cultured on choline exposed to the extract with visible deterioration of the cell wall.