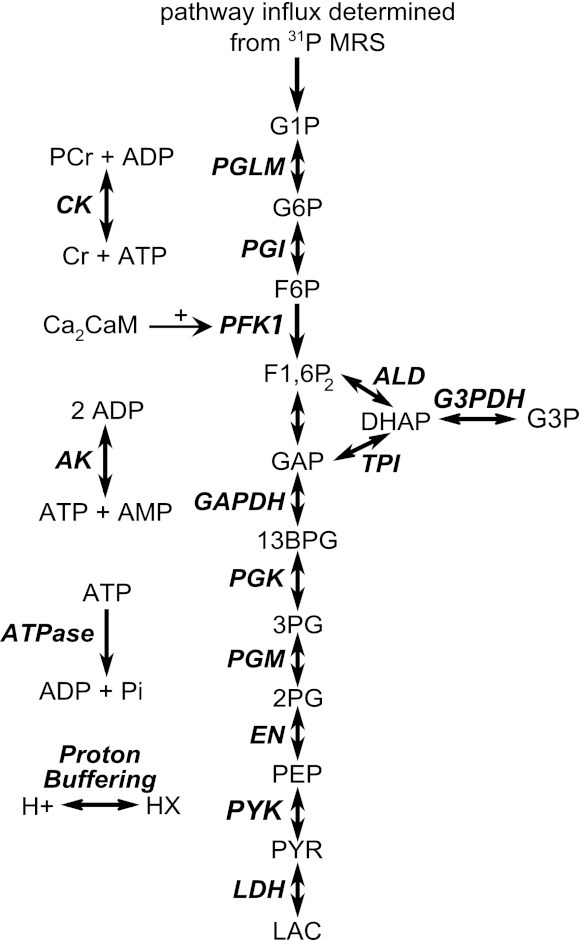
Fig. 1.
Schematic overview of the computational model. PGLM, phosphoglucomutase; PGI, phosphoglucoisomerase; PFK-1, phosphofructokinase; ALD, aldolase; TPI, triose phosphate isomerase; GAPDH, glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogeanse; G3PDH, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PGK, phosphoglycerate kinase; PGM, phosphoglyceromutase; EN, enolase; PYK, pyruvate kinase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; CK, creatine kinase; AK, adenylate kinase; ATPase, ATP hydrolysis; G1P, glucose-1-phosphate; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; F6P, fructose-6-phosphate; F1,6P2, fructose-1,6-biphophate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone-phosphate; G3P, glycerol-3-phosphate; GAP, glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate; 13BPG, 1,3-biphosphoglycerate; 3PG, 3-phosphoglycerate; 2PG, 2-phosphoglycerate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PYR, pyruvate; LAC, lactate; PCr, phosphocreatine; Cr, creatine; ADP, adenosine-diphospate; ATP, adenosine-triphosphate; Ca2CaM, calcium-calmodulin complex; AMP, adenosine-monophosphate; Pi, inorganic phosphate; HX, protons bound to cellular proton buffer.