Figure 5.
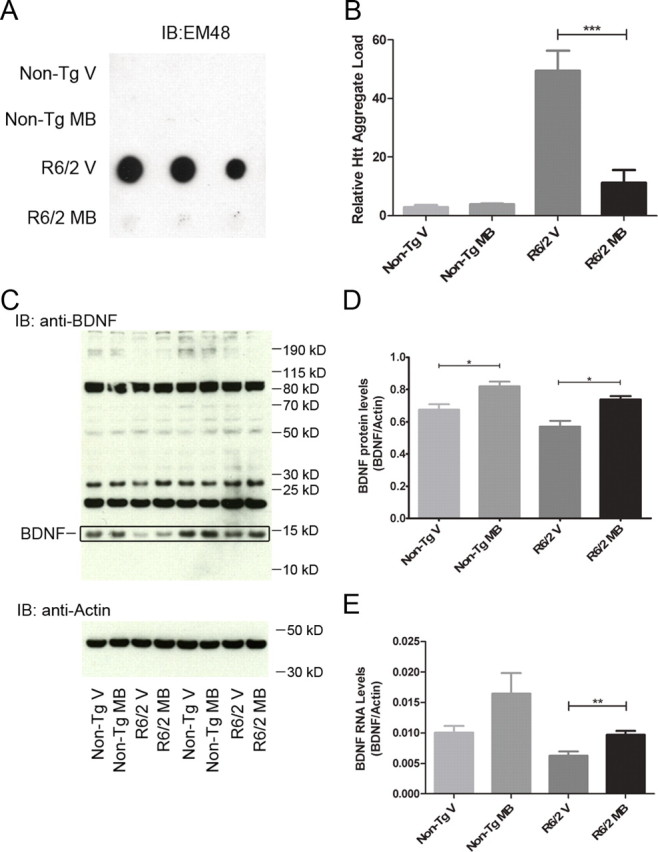
MB decreases Htt aggregation and increases levels of BDNF in R6/2 mouse model of HD. A, Striatal samples from nontransgenic littermates and R6/2 mice with vehicle or MB treatment were homogenized and analyzed for levels of insoluble Htt by filter-retardation assay. B, Densitometry of the filter-retardation assay reveals a significant decrease in the levels of insoluble Htt in the striatum of R6/2 mice when treated with MB (ANOVA, F = 29.18, p = 0.0001; Bonferroni's multiple comparison, ***p < 0.001). C, Cortical samples from nontransgenic littermates and R6/2 mice with vehicle or MB treatment were homogenized and analyzed for BDNF protein by SDS-PAGE assay and Western blot analysis. The BDNF is indicated. D, Densitometry of the SDS-PAGE analysis shows a significant increase in BDNF protein levels with MB treatment in both nontransgenic littermates and R6/2 mice (ANOVA, F = 11.35, p = 0.0002; Bonferroni's multiple comparison, *p < 0.05). Samples were normalized to actin as a control. E, Cortical samples from nontransgenic littermates and R6/2 mice with vehicle or MB treatment were homogenized and levels of BDNF mRNA quantified by qRT-PCR (ANOVA, F = 5.609, p = 0.0097; Bonferroni's multiple comparison, **p < 0.01). Error bars represent group means ± SEM. Samples were normalized to actin as a control.
