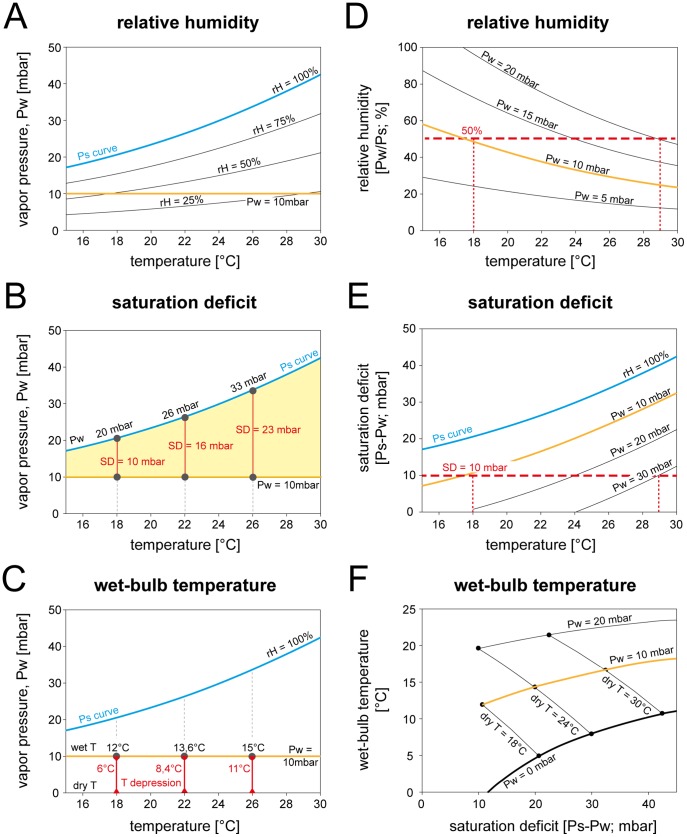
Figure 1. Calculated relationships between the key parameters of humidity and atmospheric temperature.
A. Relationship between vapor pressure, relative humidity and temperature. The relative humidity is the ratio of vapor pressure and saturation vapor pressure times 100. As the saturation vapor pressure increases with rising temperature, the relative humidity decreases when the vapor pressure is constant. B. Relationship between vapor pressure, saturation deficit and temperature. The saturation deficit is the difference between vapor pressure and saturation vapor pressure and shows the amount of water vapor required for saturation at different temperatures. As the saturation vapor pressure increases with rising temperature, the saturation deficit increases when the vapor pressure is constant. C. Relationship between vapor pressure, wet-bulb temperature and dry-bulb temperature, which is the atmospheric temperature. Temperature depression is the difference between wet-bulb and dry-bulb temperature. As the saturation vapor pressure increases with rising temperature, the wet-bulb temperature as well as the temperature depression increases when the vapor pressure is constant. D. Relationship between relative humidity, vapor pressure and temperature. E. Relationship between saturation deficit, vapor pressure and temperature. F. Relationship between wet-bulb temperature, vapor pressure and saturation deficit. At constant vapor pressure (orange line), both the wet-bulb temperature and the saturation deficit increases with rising (dry-bulb) temperature. Pw water vapor pressure, Ps saturation water vapor pressure, rH relative humidity, SD saturation deficit, dry T dry-bulb temperature, wet T wet-bulb temperature.