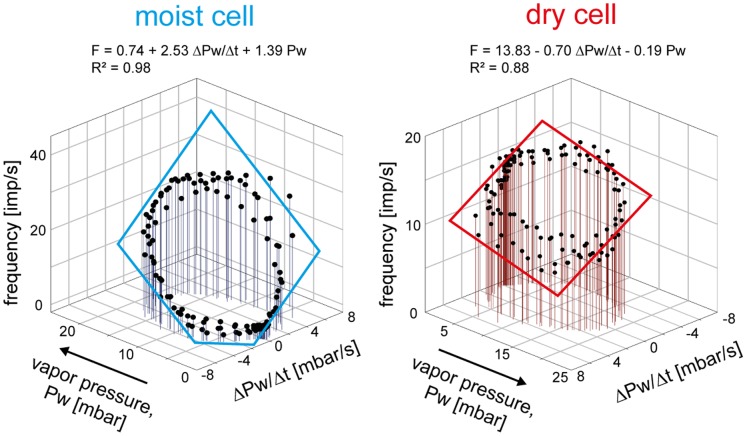
Figure 5. Humidity stimulation expressed as vapour pressure.
Impulse frequency of a moist cell and a dry cell located in the same sensillum during three consecutive oscillations in vapor pressure as a function of instantaneous vapor pressure and its rate of change. Multiple regressions which utilize three-dimensional planes [F = yo+a (ΔPw/Δt)+bPw; where F is the impulse frequency and yo is the intercept of the regression plane with the F axis reflecting the height of the regression plane] were calculated to determine the gain of the responses for the instantaneous vapor pressure (b-slope) and its rate of change (a-slope). Impulse frequency of the moist cell increases linearly with rising instantaneous vapor pressure and its rate of change, in the dry cell with falling instantaneous vapor pressure and its rate of change. R2, coefficient of determination; the number of points per plot is 130. Arrows point in the direction of increasing axis values. F impulse frequency, Pw water vapor pressure.