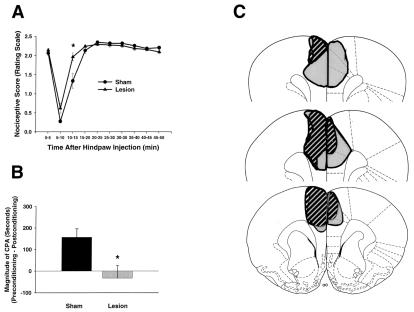
Figure 2.
Formalin-induced pain behaviors and brain lesion maps associated with rats with rostral ACC lesions (n = 8) and rostral ACC sham lesions (n = 10). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Acute formalin-induced nociceptive scores (rating scale) are shown in A. Magnitude of CPA scores are shown in B. Representations of the largest and smallest lesions in the rostral ACC lesion group are shown in C. Mean percent damage calculations for each hemisphere and a bilateral mean for each experimental group are as follows: left hemisphere, 71% ± 4%; right hemisphere, 51% ± 6%; mean, 62% ± 4%. Rostral ACC lesions completely abolished F-CPA (B) without causing a concomitant reduction in acute formalin-induced nociceptive behaviors (A). (A) *, P < 0.05, Tukey's honestly significant difference test, as compared with rats with sham lesions of the rostral ACC. (B) *, P < 0.05, Student's t test, as compared with rats with sham lesions of the rostral ACC.