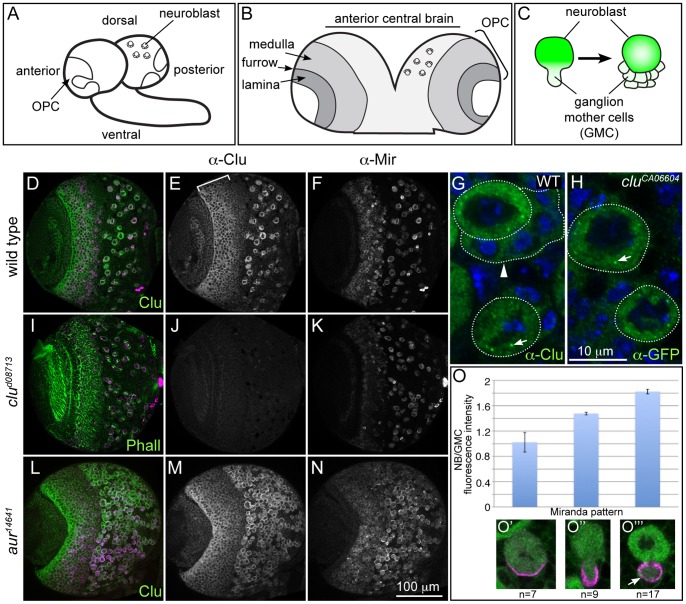
Figure 1. Clu protein is highly expressed in NBs.
(A–C) Schematics of the larval brain and NB division. A) The larval brain, showing the outerproliferative center (OPC) and central brain neuroblasts. B) The OPC consists of the medulla and the lamina separated by the laminar furrow. C) Neuroblasts (NB) repeatedly divide asymmetrically to produce daughter ganglion mother cells (GMCs) that go on to differentiate and populate the adult central nervous system. (D–F) Wild type Clu protein localization in the third instar brain. D) Clu and Mir both label the same cells. E) Clu is highly expressed in the cytoplasm of large cells in the central brain, as well as medullar neuroblasts (bracket). F) Mir antibody labeling central brain NBs and medullar neuroblasts. G) WT NBs labeled with Clu antibody. NBs (round dotted outline) contain cytoplasmic Clu, as well as distinct Clu particles (arrow). Daughter GMCs (arrowhead, outline) have markedly lower amounts of Clu. H) cluCA06604 Clu GFP-trap NBs labeled with anti-GFP antibody also show cytoplasmic Clu and Clu particles (arrow). (I–K) clud08713 mutant brains lack any detectable Clu expression. I) clud08713 mutant brain labeled with anti-Clu antibody, Mir and phalloidin. J) clud08713 lacks Clu expression but has normal Mir expression (K). (L–N) Clu is expressed in ectopic NBs formed in aur mutant larval brains. aur14641 mutant brains have a greatly increased number of Mir positive NBs (N). These NBs also label with Clu antibody (L and M). (O) Clu protein levels are decreased in GMCs compared to NBs, even when the GMC is still connected to the NB. (O’–O’’’) Clu and Mir antibody labeling denotes the NB cell cycle stage examined for Clu expression. anti-Clu - green in D, G, H, L, O’–O’”, white in E, J, M. anti-Mir- magenta in D, I, L, O’–O’”, white in F, K, N. Phalloidin (green), I. Error bars: N for D–F, I–K, L–N. H for G and H.