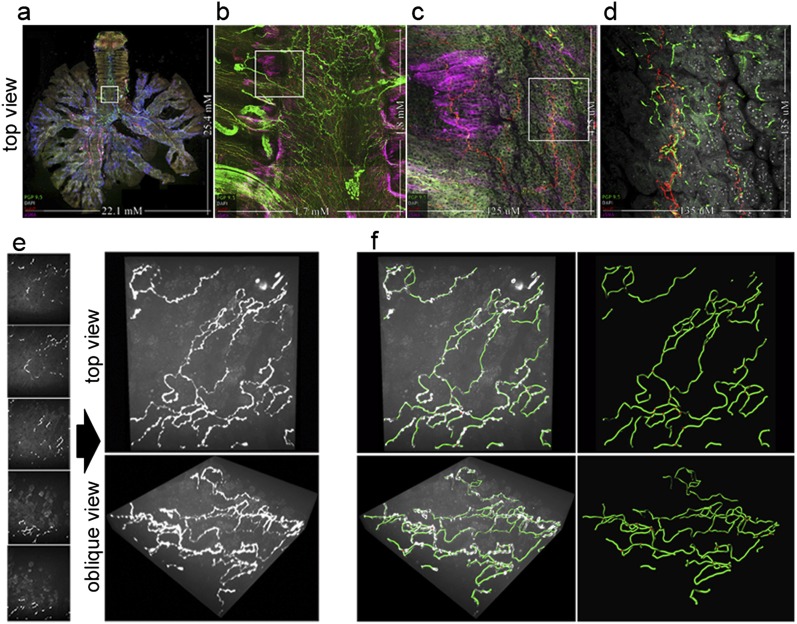
Figure 1.
Whole-organ innervation and computer mapping of peripheral nerves. (a–d) Flattened projections of three-dimensional (3D) airway images at four magnifications capturing (a) whole airway innervations up to (d) higher-resolution epithelial nerve structure. The boxed areas indicate the field of view for the next panel. Nerves are labeled with a pan-neuronal antibody, PGP 9.5 (green). The identification of tissue compartments and subtyping nerves is demonstrated using α–smooth muscle actin (pink) for airway smooth muscle, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (white) for cell nuclei, and substance P (red) for a subpopulation of sensory nerves. (e and f) Computer mapping of epithelial nerves. (e) Optical sectioning (z-stack) image series of airway epithelial nerves and three-dimensional visualization of images at orthogonal and oblique angles, using maximum intensity projection. (f) Computer nerve map (green) was overlaid on raw image data (white). After mapping, nerve structural characteristics are automatically identified and quantified. Branchpoints are shown as red spheres. See videos 1a–1c in the online supplement.