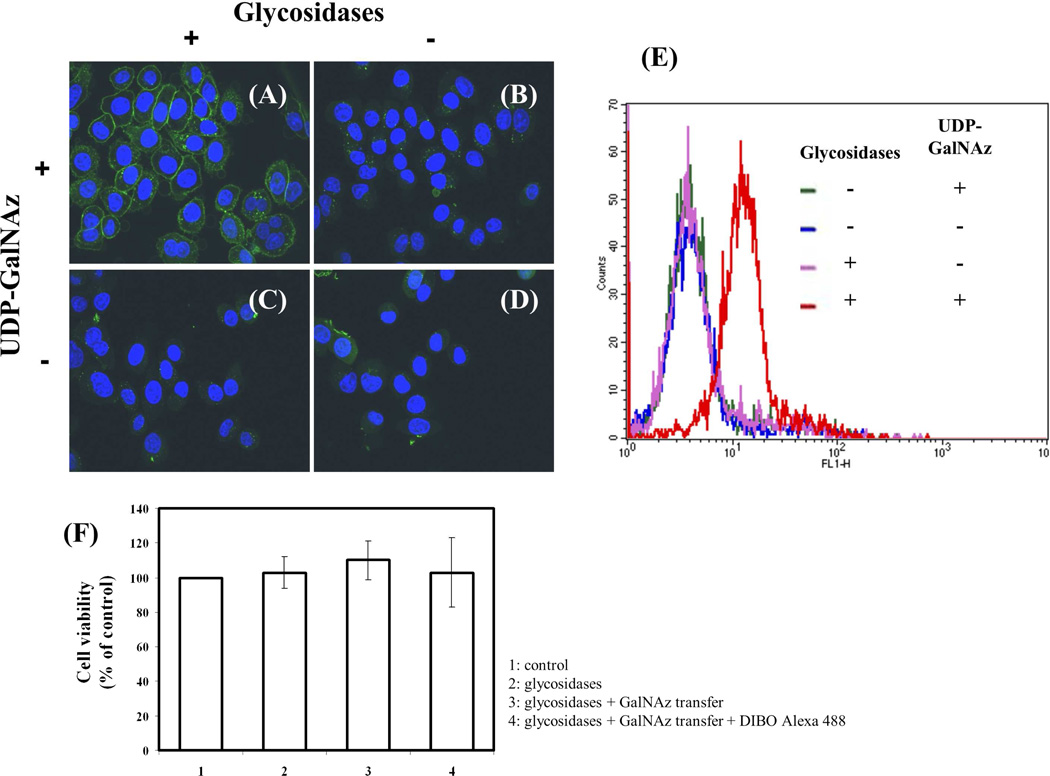
Figure 4.
Detection of cell surface terminal free GlcNAc residues using Y289L-M344H-β4Gal-T1 enzyme. After pretreatment with or without glycosidases, live cells were labeled with the Y289L-M344H-β4Gal-T1 enzyme in the presence or absence of UDP-GalNAz. After conjugation with DIBO-Alexa Fluor 488 (green fluorescent signal), the cells were washed and fixed. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342 and HeLa cell images were obtained by confocal fluorescence microscopy. Treatments were performed as follows: A: Pretreatment with glycosidases and UDP-GalNAz present; B: No pretreatment with glycosidases and UDP-GalNAz present; C: Pretreatment with glycosidases and UDP-GalNAz omitted; and D: No pretreatment with glycosidases and UDP-GalNAz omitted. E: Cell surface GlcNAc detection by flow cytometry using the mutant enzyme β4Gal-T1-M344H-Y289L. FACS analysis of HeLa cells with and without pretreatment with the enzymes sialidase and galactosidase. Negative controls are cells incubated in the absence of the donor sugar UDP-GalNAz. F: Estimation of HeLa cell viability using trypan blue method. No significant differences in cell viability were found, indicating that the labeling protocol is suitable for detection of GlcNAc on live cells.