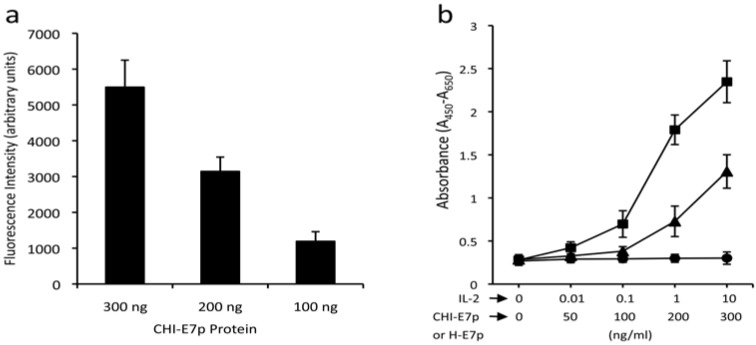
Fig. (3).
Functional characterization of the CHI-E7p protein. (a) Transmigration assay. The graph shows the chemotactic activity of the CHI-E7p fusion protein on DCs isolated from HLA-A2 (AAD) transgenic mice that were labeled with CFSE and added to the upper chamber of 24-well transwell plates (5 µm pore size) in medium X-Vivo. The lower chamber contained X-vivo with the indicated concentrations of CHI-E7p fusion protein. Fluorescence intensity was measured in a Victor® plate reader. Fluorescence intensity values measured in wells in which no protein was added to the lower chamber were subtracted from those measured in the wells containing CHI-E7p protein. The fluorescence intensity was dose-dependent. (b) Cytokine-dependent proliferation assay. Represented is the proliferation of CTLL-2 cells in response to the CHI-E7p protein. CTLL-2 cells, which depend on IL-2 for growing, were plated in 96-well plates with medium supplemented with IL-2 (squares), CHI-E7p (triangles) or H-E7p (circles) at the indicated concentrations and incubated for 48 hours. Cell proliferation was measured with the WST-1 assay and is given as absorbance at 450 nm after subtracting the absorbance at a reference wavelength of 650 nm. The CTLL-2 cells only proliferate in the presence of IL-2 or CHI-E7p, but not H-E7p. This experiment was performed twice.