Fig. 3. Removal of the CD14+ monocytes from the mononuclear fraction resulted in a loss of HUCB protective effects.
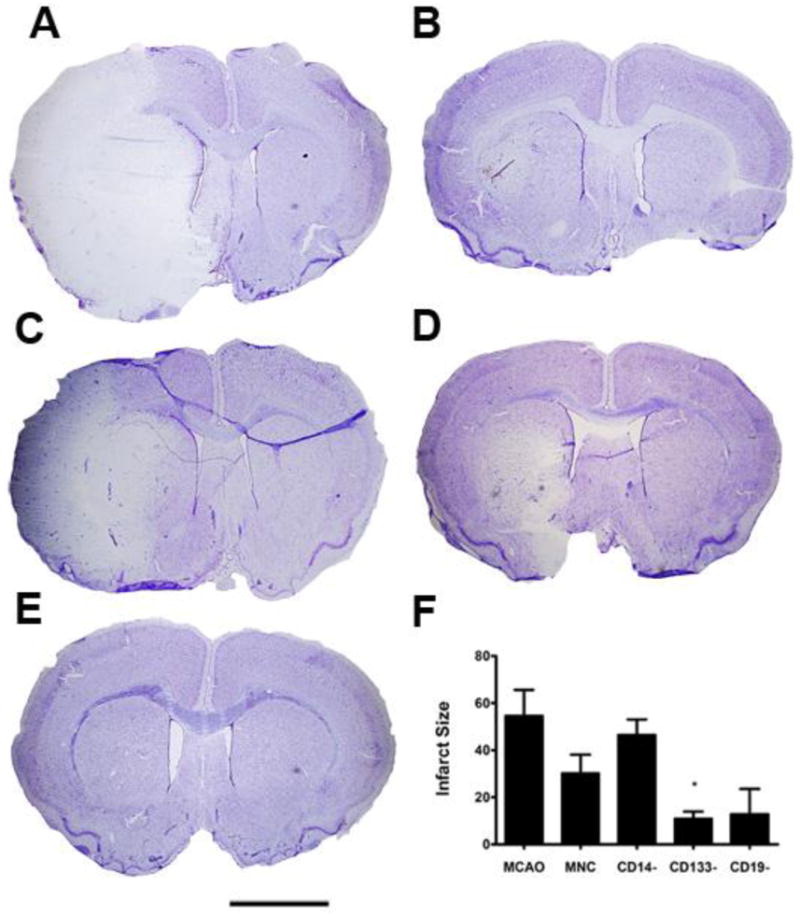
Nissl Thionin staining was used to label neurons. A) At 72 hr post-MCAO, the ipsilateral hemisphere had few thionin labeled neurons surviving, while the contral lateral hemisphere was intact. B) In the HUCB MNC treated rats, the size of the infarct was much smaller. C) When CD14+ monoyctes were removed from the MNC, there was a large infarct in the lateral striatum and overlying cortex. D) Removing CD133+ and E) CD19+ HUCB cells also appeared to decrease infarct size compared to the MCAO only controls. F) Quantification of infarct volume demonstrated that removal of CD14+ monocytes resulted in infarct size similar to the MCAO only animals while removal of the CD133+ stem cells significantly decreased infarct volume. * p < 0.05. Scale bar = 2.0 mm.
