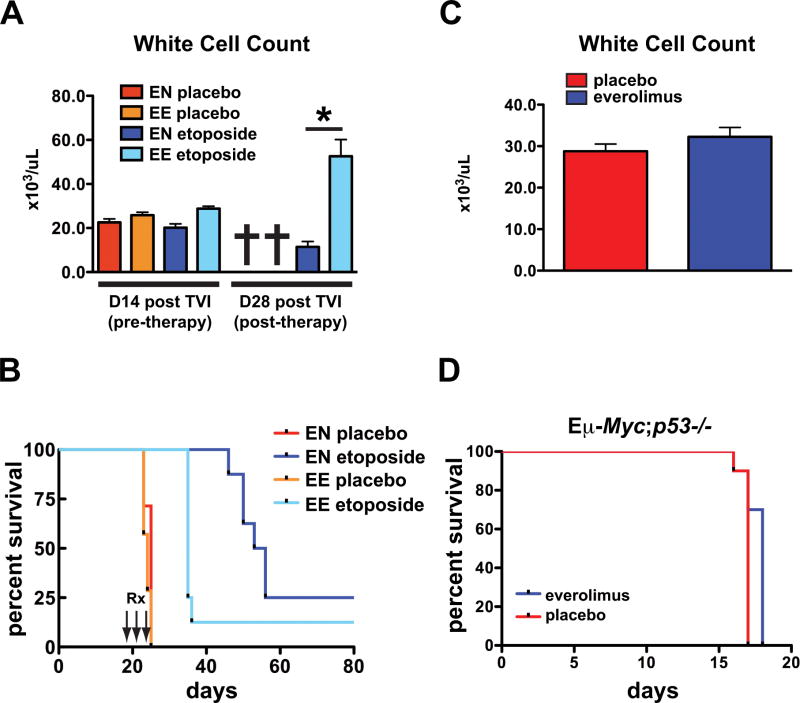
Figure 7. Everolimus resistance is associated with loss of functional p53.
(A and B) Syngeneic mice were injected with everolimus-naïve (EN) Eμ-Myc lymphoma cells (tumor#299) or equal-passage cells previously exposed to everolimus (EE). After the development of overt malignancy on day 14, mice were treated with placebo or etoposide (25mg/kg ip) on 3 consecutive days (n=7 mice per group). Surviving mice were rebled on day 28. (A) White cell counts of mice prior to therapy with etoposide at 14 days (D14) post tail vein injection (TVI) and 14 days after etoposide (D28) (p<0.001 for EN vs EE tumors treated with etoposide at D28), *=p<0.05. (B) Survival curves. Median survival was 24 days and 25 days for placebo-treated EE and EN tumors respectively and 35 days and 54.5 days for etoposide-treated EE and EN tumors (p=0.03 for EN vs EE tumors treated with etoposide). (C and D) Syngeneic mice were injected with lymphoma cells (tumor#3391 or tumor #3239) derived from spontaneously arising tumors in Eμ-Myc;p53−/− mice. Dosing with placebo or everolimus was started 72 hours after injection. (C) White cell counts of mice measured 10 days after commencement of therapy (top panel), (placebo vs everolimus, p=0.26). (D) Survival curves for everolimus-treated and placebo-treated mice (bottom panel). Median survival was 17 days in the placebo group and 18 days in the everolimus group (n=10 mice per group). Error bars represent the SEM. p values were generated using a Student’s unpaired 2-tailed t-test, *=p<0.05.