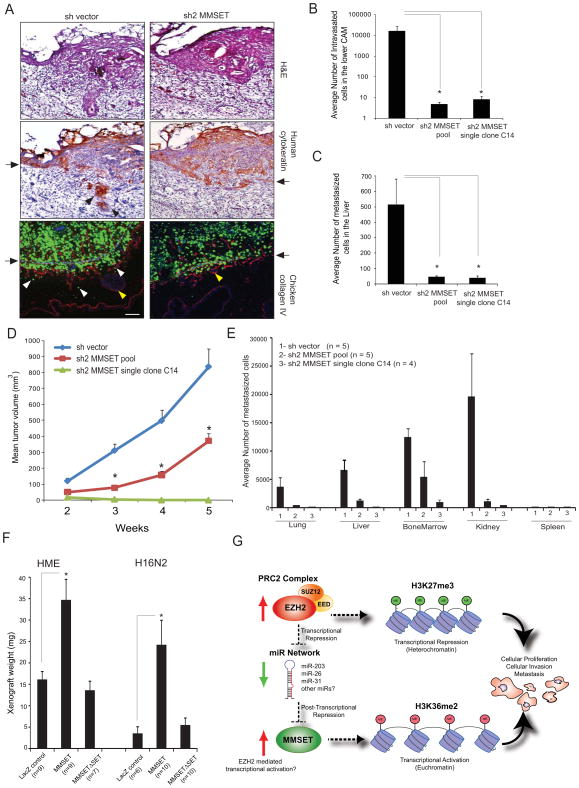
Figure 6. MMSET knockdown attenuates tumorigenesis in vivo.
(A) MMSET knockdown attenuates basement membrane invasion in a chicken CAM model. DU145 cells expressing GFP shvector control or shMMSET were engrafted atop the CAM of 11-day-old chick embryo and cultured for 3 days. Representative H&E, IHC with human specific cytokeratin, and immunofluorescence (IF) micrographs of CAM cross-sections showing DU145 cells (green) crossing the basement membrane (arrows). Red, chicken collagen IV; blue, DAPI staining for cell nuclei; arrows, basement membrane; red and white arrowheads, invaded cells; yellow arrowheads, blood vessels in CAM tissue. Scale bar (100 μm). (B) MMSET knockdown reduces cancer cell intravasation. Genomic DNA from lower CAM was isolated 3 days post-engraftment and number of intravasated cells was measured by human Alu-qPCR. (C) MMSET knockdown attenuates distant metastasis. Control or MMSET knockdown pool or single clone cells were inoculated atop CAM of 11-day-old chick embryos. Genomic DNA from lungs was extracted seven days post-inoculation and analyzed by human Alu-qPCR. Bar graph represents average cell number with ±SEM from N=7 per group. (D) MMSET knockdown attenuates DU145 tumor growth in mice. N=7 mice per group were injected subcutaneously. (E) MMSET knockdown reduces spontaneous metastasis in mouse xenograft model. Various organs and bone marrow cells were isolated from the DU145 xenografted mice after 5 weeks. Genomic DNA isolated from these organs was analyzed for metastasized cells by human Alu-qPCR. (F) Increased xenograft growth in vivo in CAM assay by HME and H16N2 cells overexpressing MMSET.*p<0.05, Student’s t-test. (G) Proposed model for the EZH2-MMSET histone methyltransferase axis in cancer. Red and green arrows indicate upregulation and downregulation respectively. Also see Figure S6.