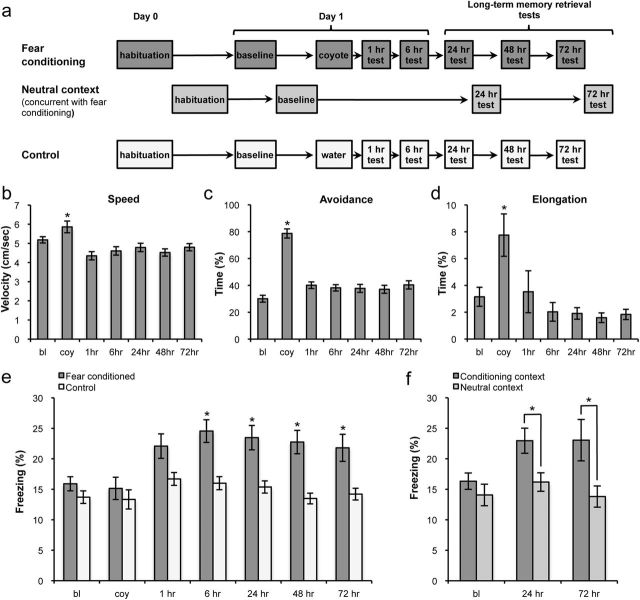
Figure 1.
a, A fear-conditioning protocol was designed with coyote urine as the US. The neutral context condition was run in a subset of fear-conditioned animals. b–d, Unconditioned responses to coyote odor in the fear-conditioned group comprising speed, avoidance, and elongation, respectively. e, Fear-conditioned animals (n = 25) froze significantly more than control animals (n = 21) exposed to water beginning at 6 h after coyote odor exposure. f, Fear memory acquisition was specific to the training context, as fear-conditioned animals did not freeze in a similar neutral context. bl, Baseline; coy, coyote odor session. Means ± SEM are shown in b–f. *p < 0.05.