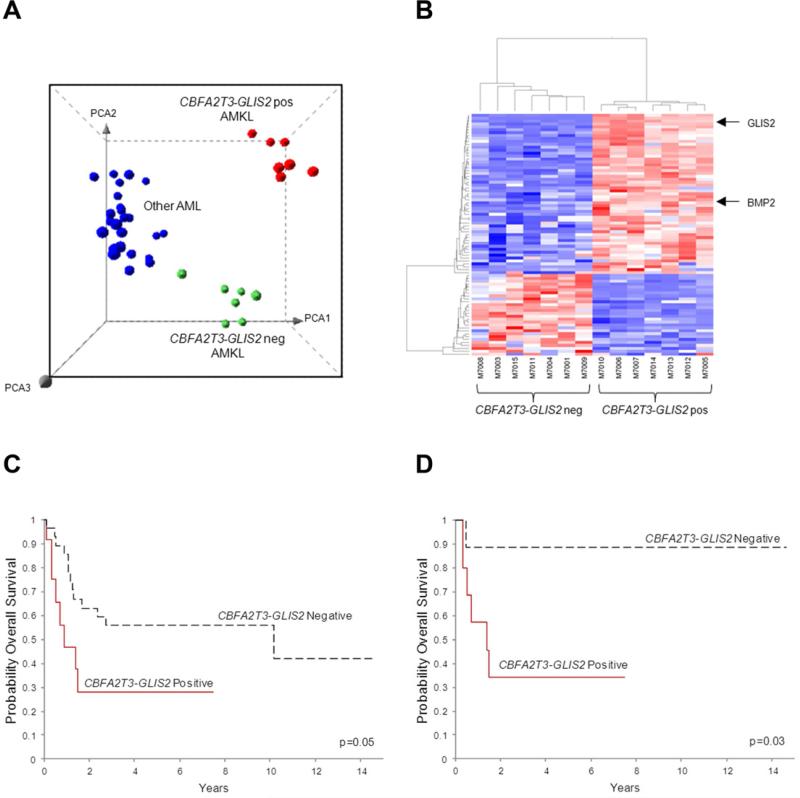
Figure 4. CBFA2T3-GLIS2 defines a unique subtype of AML with a distinct gene expression signature and poor outcomes.
(A) Principal component analysis of the gene expression profiles of the AMKL discovery cohort and 32 other non-AMKL AML samples representing all other known genetic subtypes of pediatric AML. Clusters were generated using 1000 genes selected by k-means algorithm. A detailed description of the samples included in this analysis can be found at NCBI gene expression omnibus, accession GSE35203. (B) Heat map of differentially expressed genes in the top scoring network module of CBFA2T3-GLIS2 positive and negative AMKL patient samples. For gene relationships please see Figure S3. For a detailed list of the top 500 differentially expressed the genes (not limited to this network), please see Table S7. (C) Overall survival of 40 pediatric non-DS AMKL cases treated at multiple institutions (CBFA2T3-GLIS2 negative cases n=28, and CBFA2T3-GLIS2 expressing cases, n=12). The curves for the two groups were tested by logrank method and exact test using permutation which yielded a p value of p=0.05. (D) Overall survival of 19 pediatric non-DS AMKL cases treated at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (CBFA2T3-GLIS2 negative cases, n=9, and CBFA2T3-GLIS2 expressing cases, n=10). The curves for the two groups were tested by logrank method and exact test using permutation which yield a p value of p=0.03. See also Figure S3 and Table S7.