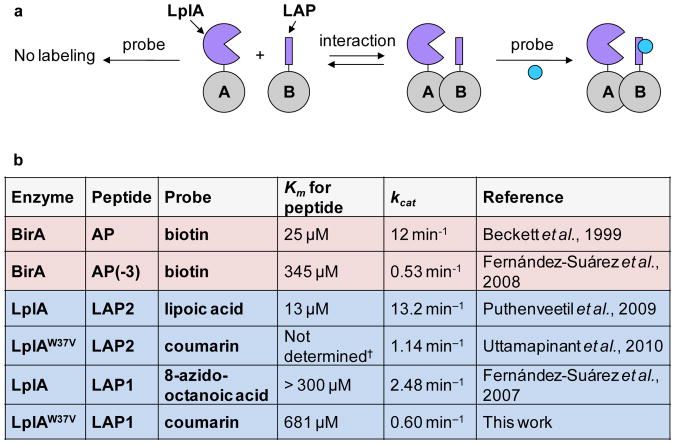
Figure 1.
Scheme for interaction-dependent PRIME (ID-PRIME) and kinetic parameters. (a) Interaction between proteins A and B promotes covalent fluorophore ligation to the fused peptide (LAP), catalyzed by the fused ligase enzyme (LplA). In the absence of an interaction, no ligation occurs. (b) Summary of kinetic parameters from previous studies and this work. Rate constants relevant to proximity biotinylation are shaded red6. Rate constants relevant to LplA ligation are shaded blue9,11,12. BirA is E. coli biotin ligase, and AP is its 15-amino acid acceptor peptide. AP(-3) is a truncated AP with 3 amino acids removed from the C-terminus6. The low affinity LAP sequence (LAP1) used for ID-PRIME is DEVLVEIETDKAVLEVP9. The high affinity LAP sequence (LAP2) used for conventional PRIME is GFEIDKVWYDLDA12. The lysine site labeled by the enzyme is underlined. †We note that, while the Km of LplA for LAP2 has not been determined in the presence of coumarin substrate, this value is expected to be similar to the 13 μM value found in the presence of lipoic acid.