Fig. 2.
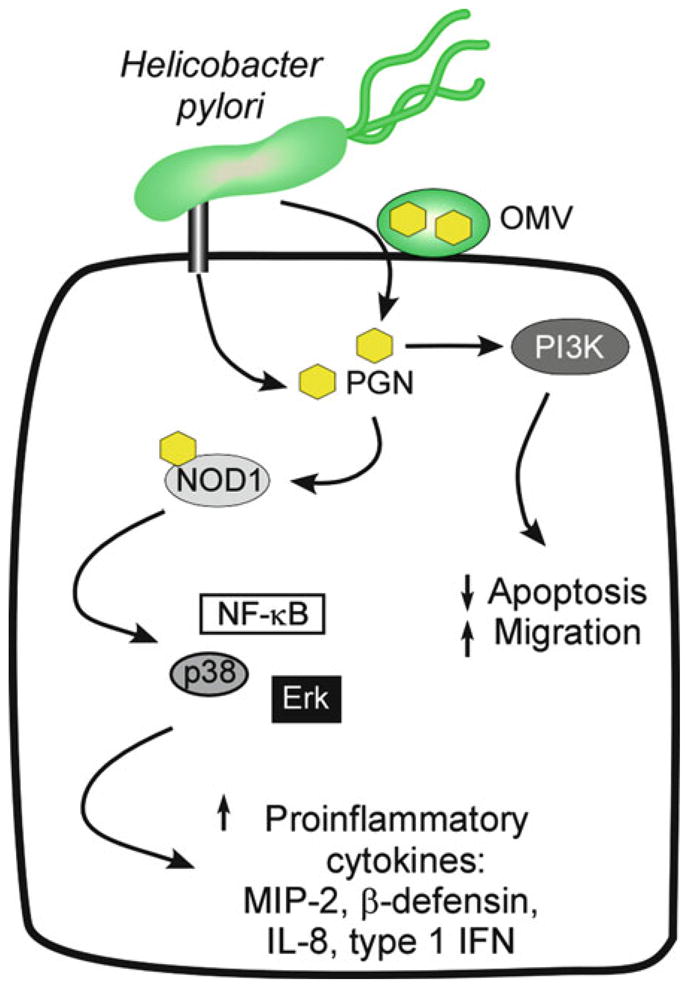
Molecular signaling alterations induced by intracellular delivery of peptidoglycan. In addition to CagA, the H. pylori cag type IV secretion system can deliver peptidoglycan (PGN) into host cells. Another mechanism of PGN delivery is via outer membrane vesicles (OMV). Delivery of PGN results in activation of the intracellular receptor nucleotide oligomerization domain 1 (NOD1) and triggers multiple signaling pathways that culminate in NF-κB activation and subsequent production of inflammatory and immune effectors, such as IL-8 and Type 1 IFN. Further, PGN can also activate PI3K, leading to decreased levels of apoptosis and increased cell migration.
