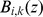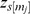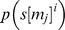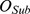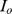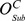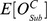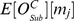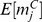|
M
|
number of bins used for discretization of observations |
|
k
|
number of bins an observation can be assigned to at the same time. |
|
n
|
number of observed metabolites |
|
t
|
knot vector that is used to define the shapes of B-spline curves |
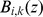
|
the probability associated with the i
th B-spline curve for the given z value and for a specific k
|
|
P
|
population of individuals |
|
s
|
an individual in the population |
|
mj
|
j
th observed metabolite |
|
s[mj]
|
the observed value for j
th metabolite for individual s
|
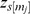
|
transformed value for s[mj] given the max and min values for mj
|
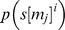
|
probability of assigning s[mj] to bin i. |
|
H(X)
|
entropy of the random variable X. |
|
I(X;Y)
|
mutual information of random variables X and Y. |
|
Sub
|
a subset of the observed metabolites |
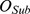
|
random variable that represents all combinations of the binned metabolite observations for Sub
|
|
C
|
random variable that represents the class variable (e.g. WT and CF) |
|
ps(o)
|
probability of observing the bin combination o for individual s
|
|
p(o)
|
probability of observing the bin combination o in population P
|
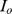
|
marginal mutual information obtained from the bin combination o
|
|
o[mj] |
the bin associated with the j
th metabolite in the bin combination array o
|
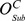
|
random variable that contains all bin combinations for metabolites in Sub that are class C -specific. |
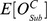
|
expected bins for metabolites in Sub for class C
|
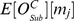
|
expected bin for metabolite j for class C found using the subset of metabolites Subj
|
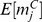
|
expected bin for metabolite j for class C found after aggregating results for different subsets |