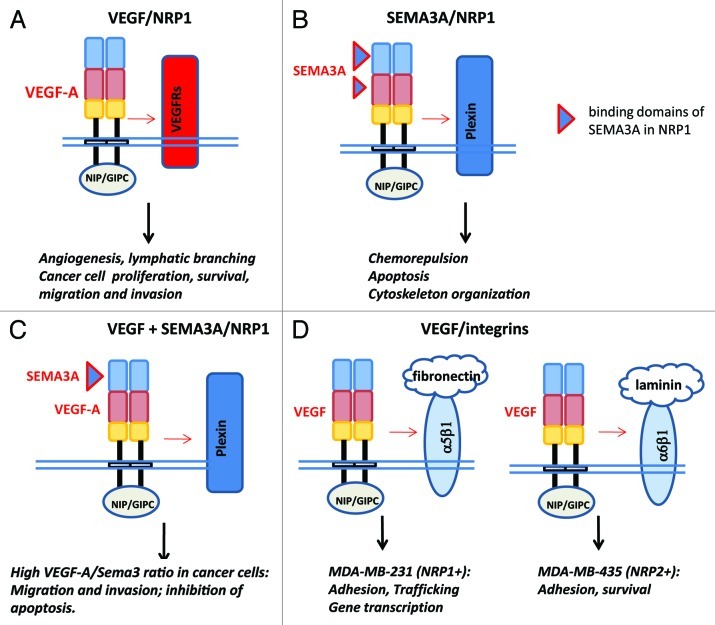
Figure 2. Schematic representation of molecular complexes involving neuropilins of the plasma membrane of cancer and/or endothelial cells. (A) Interaction between VEGF and neuropilin/VEGF receptor complexes; (B) interaction between class3 semaphorin and neuropilin/plexin complexes; (D) interaction between VEGF and neuropilin/integrin complexes. Oligomerization of NRPs molecule is induced by VEGF or SEMA3A as mentioned in Figure 1 via MAM domain (yellow box). NRPs forms complex with VEGFR (A) or plexin (B) to induce angiogenesis or repulsion and apoptosis. (C) Competition between VEGF and class3 semaphorin for neuropilin binding and activation of signaling pathway. Competition of VEGF and SEMA3A occurs at the level of b1 domain in NRP1. This mechanism is particularly relevant in tumor cell migration. (D) NRPs also participate in cell adhesion via α5β1, αvβ5 and α6β1 integrins. NRPs can also induce independent activities via interaction of the SEA domain with NIP/GIPS.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.