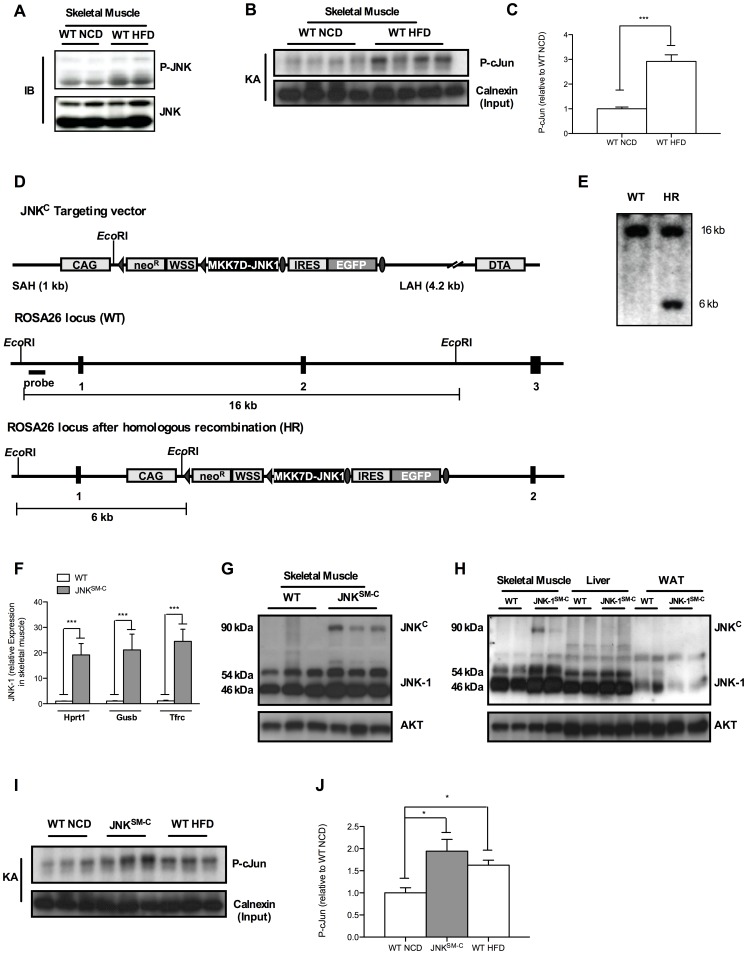
Figure 1. Muscle specific JNK overactivation.
(A) Western Blot analysis (IB) of protein lysates isolated from muscles of WT mice at 20 weeks of age when exposed to NCD and HFD using P-JNK and JNK antibodies. (B) JNK-kinase assay of protein lysates isolated from muscles of WT mice at 20 weeks of age when exposed to NCD and HFD. Calnexin antibodies were used for input control. (C) Quantitation of radioactively labeled cJun peptide in skeletal muscle of NCD fed WT and HFD WT mice. (D) Targeting strategy for the Cre-activatable JNKC construct into the ubiquitously expressed ROSA26 locus. The CAG modified STOP-EGFP-ROSA targeting vector was described elsewhere. In the unique AscI site, a fusion cDNA between the mutant MKK7D [36] and JNK-1 [37] was inserted to generate the final ROSA JNKC targeting vector. Homologous recombination between the homology arms and the genomic ROSA26 locus generated the targeted allele which was identified by Southern Blot analysis of EcoRI-digested clonal DNA using the ROSA probe [38] resulting in the 16 kb WT band besides the 6 kb targeted band as shown in (E). Such positive C57/BL6-derived ES cell clones were used to generate the ROSA JNKC mouse strain. (F) Determination of relative JNK-1 mRNA expression in skeletal muscle of WT and JNKSM-C mice by quantitative realtime PCR using Hprt1, Gusb and Tfrc as housekeeping genes (n = 8). (G) Western Blot analysis of protein lysates isolated from skeletal muscle of WT and JNKSM-C mice using JNK-1 and AKT antibodies. (H) Expression of the JNKC fusion protein only in skeletal muscle of JNKSM-C mice indicated by Western blot analysis. (I) Functionality of the JNKC construct in skeletal muscle of JNKSM-C mice was revealed by increased phosphorylation of cJun in JNK kinase assay (KA) experiments. (J) Quantitation of radioactively labeled cJun peptide in skeletal muscle of NCD fed WT, JNKSM-C and HFD WT mice. Values are means ± SEM. ***, p≤0.001.